When a sphere falls freely through a homogeneous fluid, it reaches a terminal velocity at which the weight of the sphere is balanced by the buoyant force and the frictional resistance of the fluid. Make a dimensional analysis of this problem and indicate how experimental data for this problem could be correlated. Neglect compressibility effects and the influence of surface roughness.
GIVEN
A sphere falling freely through a homogeneous fluid
Terminal velocity occurs when weight is balanced by buoyant force and friction resistance of the fluid
FIND
Make a dimensional analysis and indicate how data may be correlated
ASSUMPTIONS
Compressibility effects are negligible
Influence of surface roughness is negligible
SKETCH
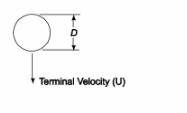
The variables which must be correlated and their dimensions are shown below

The density difference was chosen for variable 2 because we anticipate that this difference, rather than
the sphere density, will be an important parameter. Clearly, if ps = pf, then U = 0. The Buckingham ?
Theoremcan be used to correlate the variables. There are 6 variables and 3
primary dimensions. Therefore, 3 dimensionless groups will be found.
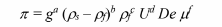
Substituting the primary dimensions into the equation
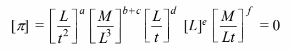
Equating the sum of the exponents of each primary dimension to zero:
For M: b + c + f = 0 [1]
For L: a – 3b – 3c + d + e – f = 0 [2]
For t: 2a + d + f = 0 [3]
There are 6 unknowns and only 3 equations, therefore, the value of the 3 exponents can be chosen for
each ?
For ?1, Let a = 0, b = 0 and c = 1
From equation [1] f = – 1
From equation [3] d = 1
From equation [2] e = 1
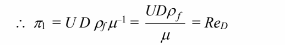
For ?2, Let a = 1, b = 1 and f = 0
From equation [1] c = – 1
From equation [3] d = – 2
From equation [2] e =
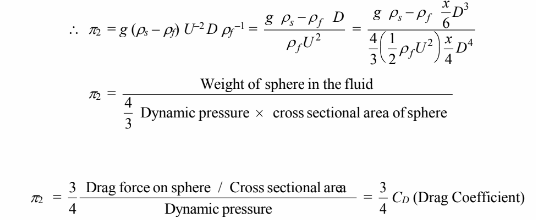
For ?3, Let a = 0, b = 1, and f = 0
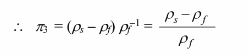
But this dimensionless group already appears in ?2. (This redundancy could have been avoided had we
chosen the weight of the sphere in the liquid in place of the two variables (?s – ?f) and g.) Therefore,
the experimental data for this problem could be correlated by
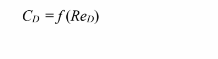
You might also like to view...
A 2.0 ?F capacitor is charged to 12. V and then discharged through 4 × 106 ?. How long will it take for the voltage across the capacitor to drop to 3.0 V?
What will be an ideal response?
Which will remain the same for two identical books, one lying flat and the other standing on an end?
A) weight only B) pressure only C) both pressure and weight D) none of the above
A group of 1.0-?F, 2.0-?F, and 3.0-?F capacitors is connected in parallel across a 24-V potential difference (a battery). How much energy is stored in this three-capacitor combination when the capacitors are fully charged?
A) 1.7 mJ B) 2.1 mJ C) 4.8 mJ D) 7.1 mJ
Radioactivity Basics: Polonium-216 decays to lead-212 by emitting what kind of nuclear radiation?
A. alpha B. beta-minus C. beta-plus D. gamma E. x-rays.