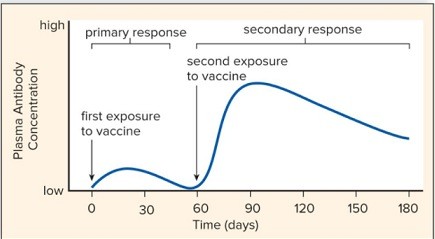
Compare the primary and secondary antibody titre responses during immunization by drawing a graph of "Plasma Antibody Concentration" vs. "Time." Indicate on the graph the time of first and second exposure. The y-axis may be quantified as low to high and need not report specific number quantities.
What will be an ideal response?
A primary response occurs after the first exposure to a vaccine. After a few days, the antibody titer slowly rises, followed by a plateau, and then a gradual decline as the antibodies bind antigen or break down. The antibody titer rises rapidly after a second exposure and then plateaus at a much higher level than during the primary exposure. A gradual decline in the concentration of antibodies then occurs.
You might also like to view...
As electrons are passed down the electron transfer chain, ________ are pumped into the ________
a. hydrogen ions / outer mitochondrial compartment b. NADH molecules / extracellular space c. electrons / cytoplasm d. hydrogen ions / mitochondrial matrix
Recently, consumption of trans fatty acids has been linked to high blood cholesterol levels and increased risk of heart disease. The food industry has responded by decreasing use of "trans fats."
Consider the following questions: (a) How do the structures and transition temperatures of trans, cis, and saturated fatty acids differ, and what are the effects on membrane fluidity? (b) Are trans fatty acids abundant in nature? (c) The major source of trans fats is hydrogenated oils. (The trans fats are produced by a side reaction during the hydrogenation process.) Why has the food industry used synthetically produced hydrogenated oils? What will be an ideal response?
The individual credited with coining the term cancer is
A) Paget. B) Hippocrates. C) Folkman. D) Rous. E) Aristotle.
The junctions between animal cells that allow the free passage of molecules smaller than approximately 1,000 daltons are called
a. tight junctions. b. plasmodesmata. c. gap junctions. d. hemidesmosomes.