By monitoring financial diaries of several of the world's poorest families, economists found that a challenge facing the poor was:
A. they did save any money to pay down debts.
B. their income fluctuated a lot, in addition to being low.
C. they often did not diversify their savings and had "their eggs all in one basket".
D. All of these are true.
B. their income fluctuated a lot, in addition to being low.
You might also like to view...
Assume that business investment spending rises, and the increase is funded by greater borrowing in the capital markets. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and current international transactions balance in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. Real GDP falls and current international transactions balance
becomes more negative (or less positive). b. Real GDP rises and current international transactions balance becomes more negative (or less positive). c. Real GDP and current international transactions balance remain the same. d. Real GDP rises and current international transactions balance remains the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
Which of these conclusions does the chart of reasons for unemployment support?
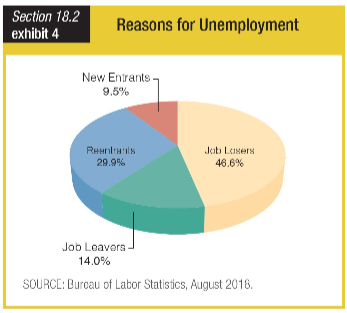
a. U.S. unemployment rates are high because no one wants to work the same job for
more than a few years anymore.
b. The only reason U.S. unemployment rates seem high is that the Bureau of Labor
Statistics counts all teenagers as new entrants.
c. Many more people are exiting the U.S. workforce than entering, which is a serious
problem.
d. About 40 percent of the unemployed either have no experience or have not worked
for a while.
After graduating from high school, Ron Willis plans to go to college. The college tuition is $15,000 a year. But, instead of going to college, Ron could take a full-time job paying $20,000. If Ron decides to go to college, what is his opportunity cost for attending for one year?
a. $35,000 b. $15,000 c. $5,000 d. $20,000
You have a value-weighted index made up of two companies. One company, we will call A, has a stock price of $25 per share and there are 10,000 shares outstanding. The other company, we will call B, has a stock price of $100 per share and has 1000 shares outstanding. What will be the percentage change in the index from a 10% increase in the share price of company A? What will be the percentage change in the index from a 10% increase in the share price of company B?
What will be an ideal response?