How many prices would a trader of a particular good need to know in a barter economy with 20 goods?
A. 100
B. 40
C. 20
D. 190
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Every point on an open-economy IS curve represents:
A) combinations of interest rates and the supply of money, which result in equilibrium in the money market. B) combinations of interest rates and levels of production, which result in equilibrium in the goods market. C) combinations of interest rates and levels of production, which result in equilibrium in the money market, the goods market, and the forex market. D) combinations of interest rates and levels of production, which result in equilibrium in the goods market and the forex market.
Which of the following is a deficit item on the balance of payments?
A) exports of merchandise B) foreign tourist dollars spent domestically C) sales of gold to foreigners D) purchases of foreign assets
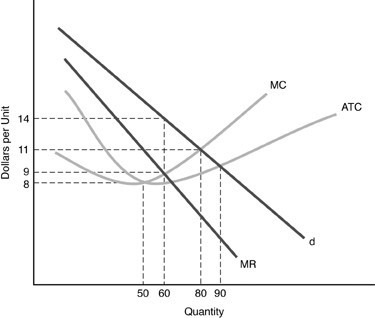 In the above figure for a monopolistically competitive firm, the total cost at the profit-maximizing point is
In the above figure for a monopolistically competitive firm, the total cost at the profit-maximizing point is
A. $540. B. $880. C. $400. D. $480.
To the extent that oligopolies differentiate their products,
A. there is the promise of new and exciting products. B. there is overproduction from society's point of view. C. they are also likely to price at marginal cost. D. they force themselves into deadlocks that waste resources.