The branch of economics which studies how households and firms interact in markets is called
A) macroeconomics. B) positive economics.
C) normative economics. D) microeconomics.
D
You might also like to view...
Suppose a U.S. computer company outsources its technical-support services to India. This will cause
A) the demand for labor in the United States to fall, lowering U.S. wage rates, and the demand for labor in India to increase, increasing Indian wage rates. B) the demand for labor in the United States to increase, lowering U.S. wage rates, and the demand for labor in India to fall, increasing Indian wage rates. C) the demand for labor in the United States to fall, lowering U.S. wage rates, and the demand for labor in India to fall, decreasing Indian wage rates. D) the demand for labor in the United States to increase, increasing U.S. wage rates, and the demand for labor in India to fall, decreasing Indian wage rates.
Suppose that for a particular firm the only variable input into the production process is labor and that output equals zero when no workers are hired. In addition, suppose that the average total cost when 5 units of output are produced is $30, and the marginal cost of the sixth unit of output is $60 . What is the average total cost when six units are produced?
a. $10 b. $25 c. $30 d. $35
The figure below shows a situation where the producers of Good X are forming an international cartel. Here, MR = Marginal Revenue, and MC = Marginal Cost. The cartel will set a monopoly price for its output.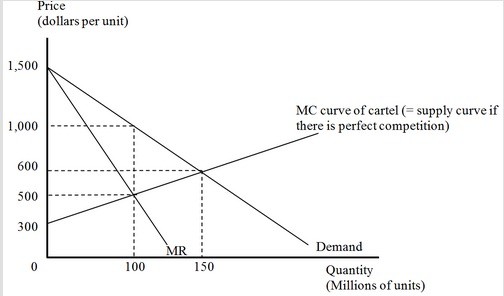 By how much would the consumer surplus fall after the formation of the cartel?
By how much would the consumer surplus fall after the formation of the cartel?
A. $5 billion B. $50 billion C. $15 billion D. $20 billion
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.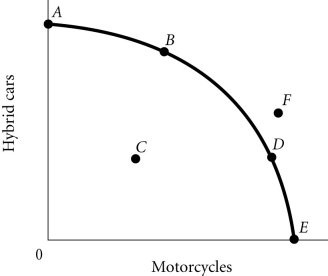 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
A. initially increases, then decreases. B. increases. C. remains constant. D. decreases.