Suppose that an increase in oil prices causes the supply curve of gasoline to shift. Using a graph, illustrate the resulting changes in equilibrium price and quantity in both the short run and the long run.
What will be an ideal response?
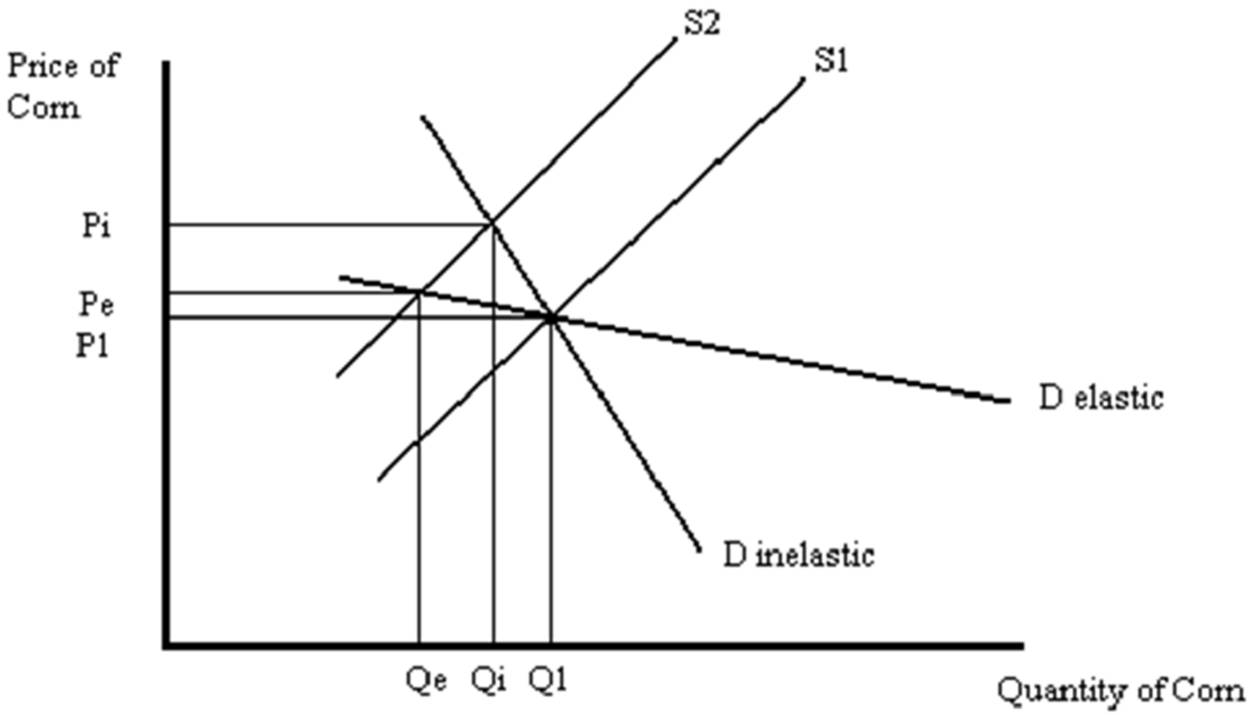
The impact of a decrease in the supply of gasoline on the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline depends upon the price elasticity of demand for gasoline. The demand for gasoline is much more inelastic in the short run than in the long run. Consumers have time to find substitutes (such as carpooling, more fuel efficient cars) in the long run. The situation is analyzed in the figure below. The market is originally in equilibrium at P1 and Q1. The decrease in the supply of gasoline is shown by the leftward shift of the supply curve from S to S'. In the short run, the relatively inelastic demand for gasoline is shown by the relatively steep slope of demand curve Dsr. In the short run then, equilibrium price becomes Psr and equilibrium quantity is Qsr. In the long run, as consumers adjust to the higher price of gasoline, demand becomes more elastic. This is shown by the relatively flat slope of demand curve Dlr. In the long run, the equilibrium price is Plr (which is less than Psr) and the equilibrium quantity is Qlr (which is less than Qsr).
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The doctrine of laissez-faire advocates an economic system with extensive government intervention and little individual decision-making. b. In capitalism income is distributed on the basis of need. c. Adam Smith was the father of socialism. d. Most real-world economies are mixed economic systems. e. The "invisible hand" refers to government economic control.
The concept of comparative advantage applies:
a. only to people with at least a high school diploma. b. only to people who are currently employed. c. to situations in which you have information about the salary levels of those with whom you are competing for a job. d. to every case of trade or exchange. e. only to goods that are sold in the domestic market.
Suppose the economy was in equilibrium, and the national government increased spending by $200 billion. Monetarist theory would predict that:
a. Both consumption and investment will fall, and net exports will rise. b. Consumption will fall, and both investment and net exports will rise. c. Any increase in government spending will be offset dollar for dollar by reduction in private demand. d. In the end, government spending, consumption, investment, and net exports will all settle back to their old position with no net change in any of them.
Labor unions ______
a. raise wages in unionized industries.
b. create labor shortages in non-unionized industries.
c. play a larger role in the current U.S. economy than in European countries such as Norway and Sweden.
d. prefer to operate in states with right-to-work laws.