Explain carefully, with a diagram, the conditions for immiserizing growth to occur. In particular, discuss the effect of the size of the country, the volume of foreign trade, the type of growth the country experiences, and foreign demand for the exports of the country.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: Immiserizing growth can occur when a country's growth is biased toward the production of the good which the country exports. If the country is large enough, the additional supply of this good will cause the international price of this good to decline relative to the prices of other goods. This effect will be more pronounced the more inelastic the foreign demand for this good is. Further, the country will stand to lose more from the worsening of the terms of trade the more this country exports the good. If the loss from the worsening of the terms of trade exceeds the gain from being able to produce more, the country experiences immiserizing growth-reduction in the well-being of the country in spite of the growth in production.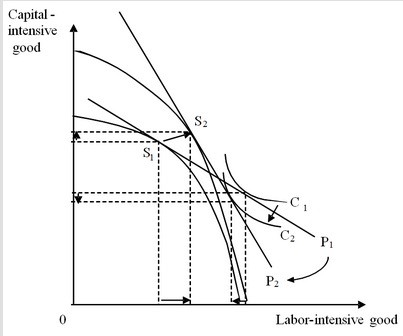
In the diagram above we see a large capital-abundant country that initially produces at S1 and consumes at C1. The country initially exports a large amount, over third of its substantial production of the capital-intensive good. The country then experiences expansion in its capital endowment (that is proportionately larger than any expansion of its other factor endowment). Its increased willingness to trade influences the international price ratio (terms of trade) and makes the price line shift from P1 to P2. Because foreign demand is price-inelastic, the price of the capital-intensive good declines by a large amount (the price line becomes much steeper). As a result of both the growth of the country's production capabilities and the change in the international price ratio, the country's production point shifts from S1 to S2. Here the country experiences immiserizing growth. Its economic well-being declines as the consumption point shifts to a lower community indifference curve, from C1 to C2.
You might also like to view...
Assume that there is a shortage of lobster and that for whatever reason prices have not risen to choke off the excess demand
Instead, the government has exhorted people to voluntary refrain from lobster consumption to "maintain a balance between supply and demand." Assume that the temporary public service announcements are "effective" and the public reduces its consumption of lobster. Explain using supply and demand analysis what should happen to the equilibrium quantity of lobster and its equilibrium price. Why would this plan not have much of an impact on the lobster market in the long run?
Price elasticity of demand is calculated as
a. the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price b. the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded c. the absolute change in quantity demanded divided by the absolute change in price d. the absolute change in price divided by the absolute change in quantity demanded e. none of the above
Which of the following will reduce the velocity of circulation of the money stock?
a. The inflation rate increases. b. The interest rate falls. c. Credit cards are used more frequently. d. More employees are paid once a week instead of once a month.
You observe that the demand for pomelo is given byQd = 5,000-10Pand the supply of pomelo is given byQs = 1,000 + 30P. What is the market equilibrium for pomelo?
A. P = 500, Q = 16,000 B. P = 200, Q = 3,000 C. P = 100, Q = 4,000 D. P = 50, Q = 2,500