Figure 18-2
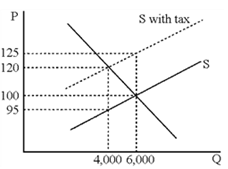
Figure 18-2 shows the widget market before and after an excise tax is imposed. The tax per widget equals ____.
A. $5
B. $20
C. $25
D. $30
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true of the market for labor?
A) In the market for labor, the supply curve is always more inelastic than the demand curve. B) In the market for labor, there is a shortage of labor at the point of intersection of the labor demand and labor supply curves. C) In the market for labor, there is a surplus of labor at the point of intersection of the labor demand and labor supply curves. D) In the market for labor, both the equilibrium wage rate and quantity of labor are determined at the point of intersection of the labor demand and labor supply curves.
Refer to Figure 23-1. If the economy is at point L, what will happen?
A) Inventories have risen above their desired level, and firms decrease production. B) Inventories have risen above their desired level, and firms increase production. C) Inventories have fallen below their desired level, and firms increase production. D) Inventories have fallen below their desired level, and firms decrease production.
Using supply and demand curve analysis, the triangular area below the equilibrium price and above the supply curve is: a. consumer surplus. b. producer surplus. c. marginal cost
d. deadweight loss.
Under a fixed exchange-rate system, in order to maintain the exchange rate:
a. governments must adopt a laissez-faire economic policy. b. all trading partners must enjoy the same level of economic growth. c. currencies must be inconvertible. d. the imports of one country must equal the exports of its trading partner. e. governments must intervene in the foreign exchange market.