Develop an expression for the ratio of the rate of heat transfer to water at 40°C from a thin flat strip of width ?D/2 and length L at zero angle of attack and a tube of the same length and diameter D in cross-flow with its axis normal to the water flow in the Reynolds number range between 50 and 1000. Assume both surfaces are at 90°C. for air flowing over the same two surfaces in the Reynolds number range between 40,000 and 200,000. Neglect radiation.
GIVEN
• Air flowing over a thin flat strip at zero angle of attack or a tube in crossflow
• Air temperature (T?) = 40°C
• Tube diameter = D
• Strip width = ?D/2
• Tube and strip length = L
• Reynolds number : 40,000 < Re < 200,000
FIND
• The ratio of the heat transfer from the strip and that from the cylinder. (qs/qt)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Radiative heat transfer is negligible
• Steady state for both cases
• The tube and strip temperatures (Ts) are 90°C
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.6 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 at 90°C Prs = 0.71
This solution follows the same procedure as the solution to
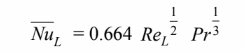
For the tube, from
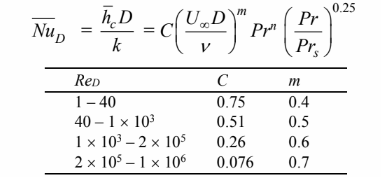
but Pr = Prs. The heat transfer rate from the strip will be 165% of that from the tube with the same
Reynolds number.
You might also like to view...
Quasar's spectral lines are:
A) emission lines with large redshifts. B) a continuum from the synchrotron radiation. C) fuzzy absorption lines from the merged light of the billions of stars. D) too complex for any interpretation. E) nonexistent, the gas so hot as to be totally ionized, so no lines are seen.
In a section of horizontal pipe with a diameter of 3.00 cm the pressure is 5.21 kPa and water is flowing with a speed of 1.50 m/s. The pipe narrows to 2.50 cm
What is the pressure in the narrower region if water behaves like an ideal fluid of density 1000 kg/m3? A) 4.00 kPa B) 7.50 kPa C) 5.82 kPa D) 6.42 kPa E) 4.61 kPa
Consider the sine of any angle between 30° and 40°. If the angle were doubled, what would happen to the sine of the angle?
a. It would double. b. It would more than double. c. It would increase but be less than double. d. In different cases, it could do any of the above.
Gaps in the asteroid belt occur at distances where
A) the density of asteroids was once so high that collisions pulverized the asteroids into dust. B) the period of an orbiting asteroid would be a simple fraction (like 1/3 or 1/4) of Jupiter's orbital period. C) the period of an orbiting asteroid would be the same as Jupiter's orbital period. D) the period of an orbiting asteroid would be the same as Mars's orbital period. E) the orbit would take the asteroid beyond the "frost line" in the solar system.