The corpus callosum is composed of
A) arcuate fibers.
B) longitudinal fasciculi.
C) association fibers.
D) commissural fibers.
E) projection fibers.
D
You might also like to view...
What are the three main components of connective tissue?
A) alveoli, fibrous capsule, and secretory cells B) collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers C) fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts D) ground substance, fibers, and cells
The longitudinal ribbons of smooth muscle visible on the outer surfaces of the colon just beneath the serosa are the __________.
a. taenia coli b. vermiform appendix c. haustra d. epiploic appendages
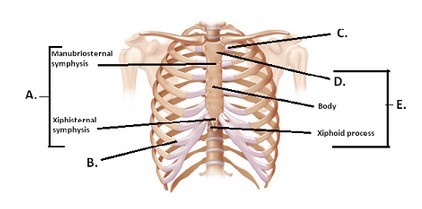 The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "A" represent?
The figure illustrates the joints and bones of the rib cage. What does "A" represent?
A. Sternocostal synchrondrosis B. Costochondral joint C. Manubrium D. Sternum E. Sternal symphyses
Contrast fast fibers with slow fibers in terms of diameter, glycogen reserves, myoglobin content, and relative abundance of mitochondria
A) Compared with slow fibers, fast fibers have a larger diameter, larger glycogen reserves, less myoglobin, and relatively fewer mitochondria. B) Compared with slow fibers, fast fibers have a smaller diameter, smaller glycogen reserves, less myoglobin, and relatively fewer mitochondria. C) Compared with slow fibers, fast fibers have a smaller diameter, larger glycogen reserves, more myoglobin, and more mitochondria. D) Compared with slow fibers, fast fibers have a larger diameter, smaller glycogen reserves, less myoglobin, and more mitochondria. E) Compared with slow fibers, fast fibers have a smaller diameter, smaller glycogen reserves, more myoglobin, and more mitochondria.