Refer to the table below for a certain product's market in Econland. Assume that the world price of the product is $6. What would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers after a quota of 400 units is imposed, compared against the total revenue received by foreign producers when a $1 per unit tariff is paid?
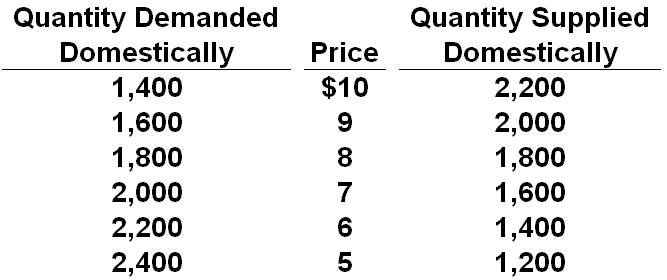
A. $0 revenue difference
B. $100 more in revenue with a quota than with a tariff
C. $400 more in revenue with a quota than with a tariff
D. $400 more in revenue with a tariff than with a quota
C. $400 more in revenue with a quota than with a tariff
You might also like to view...
The reason why inflation reduces the value of the multiplier is that part of the change in demand is
a. absorbed by price changes. b. saved rather than spent. c. matched by changes in supply. d. matched by changes in income.
If expectations are "rational," can the Fed control unemployment?
a. Yes, provided it announces policy in advance. b. Yes, if it affects the aggregate demand curve. c. No, because aggregate supply is vertical even in the short run. d. No, because only fiscal policy can affect unemployment.
If the Fed decreases the money supply,
a. aggregate demand and aggregate supply both increase. b. aggregate demand increases, which leads to movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve. c. aggregate demand decreases, which leads to movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve. d. aggregate supply increases, which leads to movement along the aggregate demand curve. e. aggregate supply decreases, which leads to movement along the aggregate demand curve.
If the money interest rate is 7 percent and the inflationary premium 4 percent, the real interest rate is
a. -3 percent. b. 3 percent. c. 4 percent. d. 7 percent.