Which of the following is not a desirable characteristic in an economy?
A. rapid increase in the general price level
B. low unemployment
C. growing per-capita output
D. population growing slower than output
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If a firm is experiencing constant returns to scale
a. long-run average total cost neither rises nor falls as production increases b. average fixed cost is zero c. the increase in average variable cost is exactly offset by a decrease in average fixed cost d. the decrease in average variable cost is exactly offset by an increase in average fixed cost e. long-run average total cost is zero.
The point at which buyers and sellers "agree" on the quantity of a good they are willing to exchange at a given price is called:
A. equilibrium. B. maximization. C. optimization. D. market collapse.
New Keynesian inflation dynamics predicts that an increase in aggregate demand will generate, in chronological order
A. a rightward shift in a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run increase in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), an upward movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level. B. an leftward shift in a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run decline in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), an upward movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level. C. a leftward movement along a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run decline in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), a downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve, and a decrease in the price level. D. a rightward movement along a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run increase in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), an upward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 16.3 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 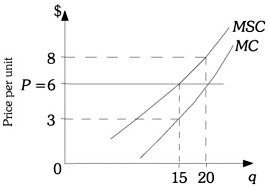 Figure 16.3Refer to Figure 16.3. If this firm is maximizing profits and is not required to take into account damages, it will produce
Figure 16.3Refer to Figure 16.3. If this firm is maximizing profits and is not required to take into account damages, it will produce
A. 0 units of output. B. 6 units of output. C. 15 units of output. D. 20 units of output.