The circuit shown in Figure P10.38 is used to switch a relay that turns a light off and on under the control of a microcontroller. The relay dissipates 0.5W at 5 VDC. It switches on at 3 VDC and off at 1.0 VDC. What is the maximum frequency with which the light can be switched? The inductance of the relay is 5 mH, and the transistor saturates at 0.2 V, V? = 0.8 V.

Find:
The maximum of frequency with which the light can be switched
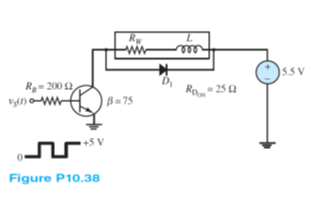
The maximum frequency (fmax) should allow the stored energy in the relay dissipates in RW and the voltage of the relay reaches 1(V) that cuts off the relay. If the switching frequency goes above the fmax the voltage of the relay remains high and the light stays ON

You might also like to view...
To reduce the possibility of carbide precipitation, use as high a welding current setting as possible and/or travel as fast as possible along the joint to help reduce carbide precipitation.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
All of the following place strain on system capacity, except for:
Multilevel stairs must be constructed of straight stair flights.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
In the circuit shown in Figure P9.50, R must maintain the Zener diode within its specified limits. If
Vbatt = 15 ± 3 V, Ro = 1,000 ?, Vz = 5V,4 mA ? Iz ? 18 mA,
determine the minimum and maximum values of R that can be used.
.png)