The number of generations it takes for an allele to become fixed or lost in a population depends on population size. There are three populations associated with the frequency of the ? allele and its change in frequency. Which population(s) show dramatic change in ? allele frequency and what are these changes? Population 1 = brown mouse (top line); Population 2 = middle line; population 3 =
white mouse (bottom line).
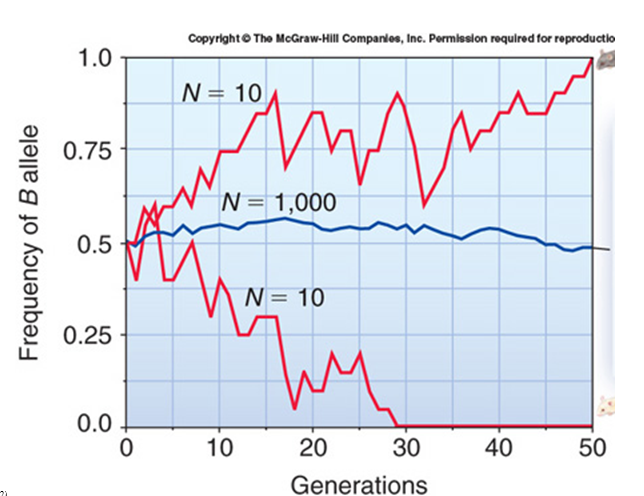
A. Population 1; it shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all brown mice.
B. Population 3; it shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all white mice.
C. Population 2; it shows an increase in the frequency of the ? allele after 50 generations.
D. Population 1; it shows a fixation of the ? allele resulting in all brown mice and Population 3 shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all white mice.
E. Population 1, 2, and 3 all show drastic changes in ? allele frequency after 50 generations, with the complete elimination of the ? allele in all three populations.
D. Population 1; it shows a fixation of the ? allele resulting in all brown mice and Population 3 shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all white mice.
You might also like to view...
Why do cells use monosaccharides for cellular fuel?
What will be an ideal response?
Which is not a characteristic of Helicobacter pylori?
A. Produces urease to buffer stomach acidity B. Gram-negative C. Produces enteroxin that causes diarrhea D. Lives in the stomach E. Curved rods
In butterflies, males are the ________ sex
A) homozygous B) heterozygous C) homogametic D) heterogametic E) hemizygous
________ are long, slender sclerenchyma cells that usually form strands.
A. Collenchyma cells B. Tracheids C. Fibers D. Sclereids