How much data can be “in flight” between a sending ground station, a satellite, and a receiving station? To find out, compute the delay-throughput product for a GEO satellite network that operates at 3 Mbps. Assume that the satellite orbits at 20,000 miles above the earth, and that radio transmissions propagate at the speed of light.
What will be an ideal response?
Bits present in a network = D x T, where D is delay and T is throughput measured in bits per
second
The delay in GEO satellite network is the time traveled from a source (transmitter) to a destination
(receiver). The distance traveled by signal is 2 times distance of a GEO from the earth, which is
2x20,000 = 40,000 miles. The time taken to travel this distance, t = distance/speed. We can assume
throughput T as 3 Mbps, assuming the bandwidth is fully utilized without any congestion or packet-
drops. Reader is encouraged to utilize these facts/numbers and calculate the number of bits present
in the network
You might also like to view...
Review each constraint and identify its characteristics: present vs. future, internal vs. external, and mandatory vs. desirable.
What will be an ideal response?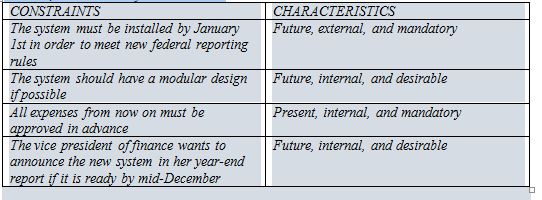
Write the function header for function add1AndSum that takes an integer built-in array parameter oneTooSmall and a second parameter representing the array’s size and returns an integer.
What will be an ideal response?
The shorthand property for border-radius can specify four values in a clockwise direction as follows: ____.
A. top-left, top-right, bottom-right, bottom-left B. bottom-left, bottom-right, top-right, top-left C. top-right, top-left, bottom-left, bottom-right D. bottom-right, bottom-left, top-left, top-right
Which of the following is not that important when considering what printer will be used when printing a banner?
A) The amount of ink or toner that will be used to print the banner B) How close to the edges of the paper the printer can print C) Whether the printer can handle the large paper size often required for a banner D) Whether you have a printing service available if your printer will be able to print the banner