If price were lowered from $10 to $8 and quantity demanded rose from 50 to 51, calculate elasticity; state whether demand is elastic, unit elastic, or inelastic; and find how much total revenue was when price was $10 and $8.
What will be an ideal response?
P1 = 10; P2 = 8; Q1 = 50; Q2 = 51.
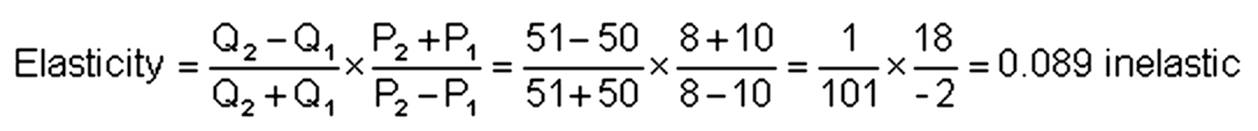

You might also like to view...
To compensate for the possibility of indirect crowding out, a government engaging in expansionary policy aimed at eliminating a recessionary gap could
A) reduce taxes rather than increase government spending. B) increase spending less than the simplest Keynesian model would predict. C) both reduce taxes and reduce spending to be able to achieve full employment. D) increase spending more than the simplest Keynesian model would predict.
Income equality has
A) decreased in the United States as manufacturing has increased. B) narrowed within countries but increased across countries. C) increased within countries but has narrowed across countries. D) not changed in the advanced economies over the past 50 years. E) increased in developing economies as manufacturing has decreased.
A differentiated product has
A) many perfect substitutes. B) no close substitutes. C) no substitutes of any kind. D) close but not perfect substitutes. E) many different complements.
When marginal revenue is positive, total revenue ________ when output increases and demand is ________
A) decreases; elastic B) decreases; inelastic C) increases; elastic D) increases; inelastic E) does not change; unit elastic