In the money market, how is the adjustment to equilibrium brought about in the short run and in the long run?
What will be an ideal response?
In the short run, the nominal interest rate adjusts to restore equilibrium in the money market. In the long run, however, the nominal interest rate equals the real interest plus the inflation rate, so it cannot freely adjust to restore equilibrium in the money market. In the long run when the economy is at full employment, the price level changes to restore equilibrium in the money market.
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 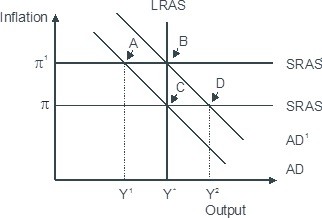
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Which of the following will not change the demand for movie tickets?
A) A change in the cost of babysitting services B) A change in the incomes of moviegoers C) A change in the price of movie tickets D) A change in the quality of television programs E) A change in the quality of movies
Default risk arises from the fact that
A) borrowers differ in their ability to repay in full the principal and interest required by a loan agreement. B) the bond price drops when interest rates rise. C) it is inherently riskier to wait for a capital gain than to receive an immediate interest payment. D) interest rates are far more likely to go up than to go down.
Which of the following is false? a. A positive statement must be testable but need not be true
b. A hypothesis is a normative statement. c. Normative analysis involves subjective, non-testable statements. d. The majority of disagreements in economics stem from normative issues.