Under monopoly, a firm:
a. is a price taker.
b. maximizes profit by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue.
c. will shut down in the short-run if price falls short of average total cost.
d. always earns a pure economic profit.
b
You might also like to view...
Use the aggregate expenditures model and the following values to answer the next question.AMPCIGT$3500.75$400$400$200Determine equilibrium consumption for this economy.
A. $3,350 B. $3,200 C. $3,000 D. $2,850
When a good is nonexcludable, then individuals
A. will purchase the good for less than it cost to produce. B. can obtain the benefits of the good without paying for it. C. have an incentive to become free riders. D. will purchase more than the optimum amount. E. b and c
Draw a graph with food on the horizontal axis and shelter on the vertical axis.A. Now sketch in a budget line such that the relative price of food to shelter is 2, the absolute price of shelter is 10, and the nominal income level is $100. Label the budget line A.B. Next, the nominal income stays the same, the absolute price of shelter is cut in half, and the absolute price of food is unchanged. Sketch in the new budget line and label it B.C. Next, the absolute prices are where they were when the problem started and the nominal income increases to 150. Draw a new budget line for this data and label it C.D. Next, the nominal income is again $100, the relative prices are as they were at the beginning and the absolute prices are cut in half. Draw a new budget line on the graph and label it
D.E. Next, the absolute price of shelter falls to $5 and the absolute price of food and the income stay where it was at the beginning. The relative price of food to shelter also stays at 2. Explain why this is a logical contradiction. What will be an ideal response?
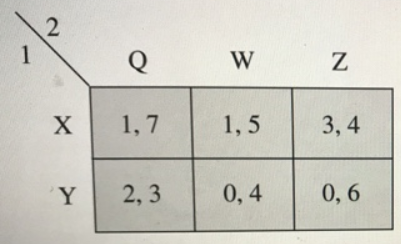
Consider the game above. at the mixed strategy equilibrium, the probability that player 2 assigns on Z =