The concept of "demand" in economics refers to
A) the different quantities of a good or service people will buy at different possible prices.
B) the different types of goods and services that people of different income levels want to buy.
C) how changes in the prices of all goods affect people's buying behavior.
D) changes in people's consumption behavior over time.
A
You might also like to view...
The Fed uses a "core" price index, one that excludes food and energy prices to measure inflation. It does so because
A) food and energy have inelastic demand curves and consumers will buy them regardless of their price. B) food and energy prices have wide swings that are not related to the causes of general inflation. C) food and energy prices do not change all that much during the short run, so are irrelevant to the calculation of inflation. D) it wants to avoid the blame for high gasoline prices causing inflation.
Assume that Jamal is a single parent who is in poverty. He receives food stamps and Medicaid. For every $100 that he earns, Jamal loses $35 in food stamps and $20 in Medicaid benefits. Also, Jamal's income is taxed at a rate of 10%. Then, Jamal's total tax rate is
a. 45 percent b. 55 percent c. 65 percent d. 70 percent
If aggregate demand shifts rightward more than expected...
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the diagram. Rational expectations theory says that a fully anticipated shift in aggregate demand from AD 1 to AD 2 will:
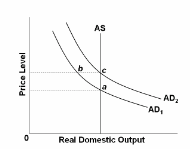
A. move the economy from a to b to c.
B. move the economy directly from a to c.
C. move the economy from a to a new equilibrium at b.
D. shift the AS curve to the right.