How does the skin act as a barrier to microbial invasion?
A) It releases B cells and T cells to fight infections.
B) Dendritic cells patrol the skin's surface, producing secretions that inhibit microbe growth.
C) Dead skin cells are packed with keratin, an antibacterial protein that punches holes in bacterial membranes.
D) Sweat and sebaceous gland secretions inhibit bacterial growth.
D
You might also like to view...
One reason food is refrigerated to control microbial growth is because irreversible cell damage is more likely to occur at low rather than high temperatures
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
Why do some seeds have to pass through an animal’s digestive tract in order to germinate?
a. The animal digests the seed coat. b. There is a lack of oxygen. c. There is a lack of sunlight. d. The temperature is appropriate.
What is the ?2 value for a chi-square test for goodness of fit of the null hypothesis?
In Drosophila, singed bristles (sn) and carnation eyes (car) are both caused by recessive X-linked alleles. The wild-type alleles (sn+ and car+) are responsible for straight bristles and red eyes, respectively. A sn car female is mated to a sn+car+ male and the F1 progeny are interbred. The F2 are distributed as follows:
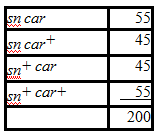
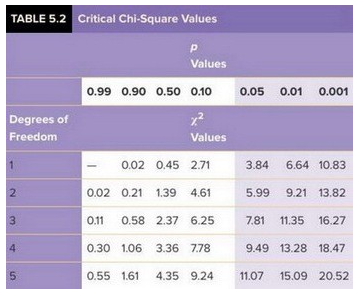
A) 0.5
B) 1.0
C) 2.0
D) 0.4
E) 20
Plastids are storage organelles. A chloroplast is a type of plastid. What does a chloroplast store?
A) Energy B) Chlorophyll C) Carbon D) Electrons