The current account balance equals
A) net exports + net transfers + net interest.
B) net exports + net transfers.
C) net exports - net transfers + net interest.
D) net exports - net transfers - net interest.
E) net exports + net transfers - net interest.
A
You might also like to view...
A more complex view of the incentives facing a bureaucrat _____
a. shows that bureaucrats might prefer to maximize their discretionary budget over their total budget b. shows that bureaucrats might prefer to always act in the public interest, if they believe in their bureau's mission. c. shows that the incentives facing a bureaucrat are simple and never conflict with one another. d. shows that the bureaucrats may about increasing their own income but their power and prestige
Lorenz curves tell us about the
A. absolute distribution of income. B. poverty line. C. incidence of malnutrition. D. relative distribution of income.
The existence of an inflationary gap should cause
A. wages to fall. B. prices to fall. C. unemployment to rise. D. net exports to rise.
Exhibit 14-6 Aggregate supply curve
?
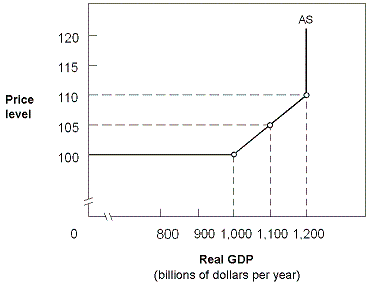
A. there are no more workers available at any wage rate to increase real GDP. B. the price level remains constant. C. the only workers available would demand higher wage rates. D. the economy is experiencing low employment and low production.