Refer to the graph shown, which depicts a perfectly competitive firm. If the price of the product is $3: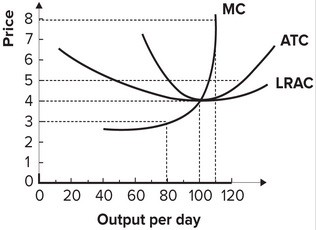
A. the firm may continue to operate in the short run but will exit the industry in the long run.
B. the industry will be in long-run equilibrium.
C. new firms will enter the industry.
D. the firm will just cover its opportunity cost of production.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Catherine is risk-averse. When faced with a choice between a gamble and a certain level of wealth she will
A) always prefer the gamble. B) always prefer the certain level of wealth. C) prefer the gamble if the expected utility from it is higher than the utility from the certain level of wealth. D) prefer the certain level of wealth if the expected utility from the gamble is higher than the utility of the certain level of wealth.
Using the liquidity-preference model, when the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, a. the equilibrium interest rate decreases
b. the aggregate-demand curve shifts to the left. c. the quantity of goods and services demanded is unchanged for a given price level. d. the short-run aggregate-supply curve shifts to the right.
Price ceilings which lead to shortages will impose costs on society because they
A. will lead to long waiting lines B. may result in black market prices, which are higher than the market-determined price would be. C. lead to a smaller quantity offered on the market. D. do all of the above.
As the Fed responded to the financial crisis that followed the collapse of the housing market, certain banks were deemed too:
A. large to fail, and were consequently purchased by the government. B. small to fail, as they were easy to save. C. large to stay afloat, as they would be too costly to save. D. large to fail, as their failure would carry the risk of causing a domino effect in the highly integrated financial system.