Suppose that in a market for used cars, there are good used cars and bad used cars (lemons). Consumers are willing to pay as much as $9,000 for a good used car but only $3,000 for a lemon
Sellers of good used cars value their cars at $7,500 each and sellers of lemons value their cars at $1,500 each. Buyers cannot tell if a used car is reliable or is a lemon. Based on this information, what is the likely outcome in the market for used cars?
A) Sellers of lemons will drop out of the market.
B) Sellers of good used cars will drop out of the market.
C) Used cars will sell for $6,000.
D) Sellers of good used cars will incur losses.
B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following would cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right?
a. An increase in the price level b. A decrease in the price level c. An increase in government purchases d. An increase in taxes e. An increase in the interest rate
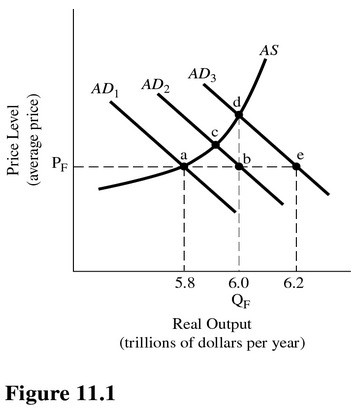 Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1, full-employment output is $6.0 trillion, and the MPC is 0.75. The spending fiscal stimulus needed to reach full-employment equilibrium is
Refer to Figure 11.1. Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1, full-employment output is $6.0 trillion, and the MPC is 0.75. The spending fiscal stimulus needed to reach full-employment equilibrium is
A. $0.4 trillion B. $2 trillion. C. $1 trillion. D. $0.1 trillion.
Within the framework of the Keynesian model, if aggregate expenditures exceed aggregate output, then:
A. the inventories of firms would decline, and the firms would expand output in order to restore their inventories to desired levels. B. the inventories of firms would increase, and the firms would reduce output until inventories were cut back to the desired level. C. the current level of income would persist in the future. D. firms would reduce their investment, and the economy would fall into a recession.
Inflation and unemployment
A. are a focus of microeconomics. B. are the focus of normative economics. C. are a focus of positive economics. D. are a focus of macroeconomics.