Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
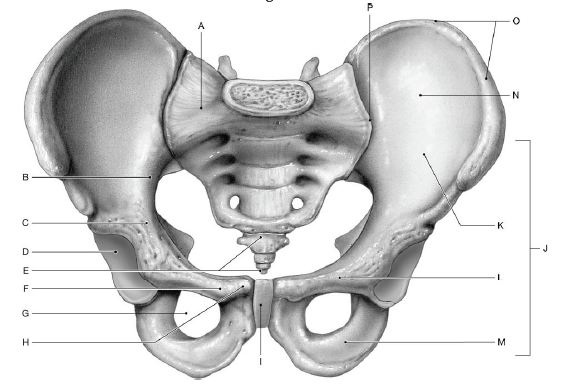
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
1) Sacrum
2) Arcuate line
3) Pectineal line
4) Acetabulum
5) Coccyx
6) Pubic tubercle
7) Obturator foramen
8) Pubic crest
9) Pubic symphysis
10) Hip bone; coxal bone
11) Ilium
12) Pubis
13) Ischium
14) Iliac fossa
15) Iliac crest
16) Sacro-iliac joint
You might also like to view...
A bacterial infection that is often fatal in burn patients is called
A) sepsis. B) necrosis. C) toxis. D) pernicious. E) noxious.
The interstitial cells in the testes
A. undergo mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. B. support and protect the developing sperm cells. C. secrete testosterone. D. convert fructose to glucose to nourish the sperm. E. form the lining of the seminiferous tubules.
Pinocytosis and potocytosis are types of
A) endocytosis and exocytosis. B) phagocytosis. C) exocytosis. D) exocytosis and phagocytosis. E) endocytosis.
Rapid removal or destruction of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
A. is necessary for synaptic transmission. B. generates local potentials in the presynaptic terminal. C. may lead to action potentials. D. may stop exocytosis. E. may affect the ability of the postsynaptic membrane to generate action potentials.