What matters in Economics is:
a. how much gain a transaction yields.
b. how the gains from a transaction are split between the buyer and the seller.
c. how much gain the buyer realizes from a transaction.
d. that the transaction between a buyer and a seller takes place.
D
You might also like to view...
The typical short-run production function is incapable of distinguishing among the different types of labor that might be hired by the firm
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A friend tells you that his income has risen every year by 5 percent. At the same time, prices, on average, have risen by 5 percent. Your friend claims he is better off. Your friend
A. Has experienced an increase in real income only. B. Really is better off as he suggests. C. Has experienced an increase in nominal and real income. D. Is experiencing money illusion.
Which of the following will increase macroeconomic equilibrium real gross domestic product?
A. a decrease in taxes B. an increase in input prices C. a decrease in government spending D. a decrease in productivity
Refer to the graph below. If the economy is initially at equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1 and there is a tax cut, then, from a skeptical mainstream perspective, the immediate impact is that aggregate:
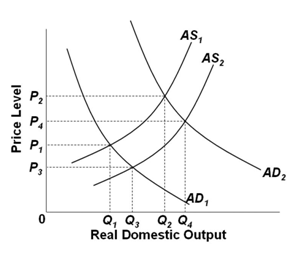
A. Demand would increase to AD2 and aggregate supply would increase to AS2
B. Demand would increase to AD2 and aggregate supply would remain at AS1
C. Supply would increase to AS2 and aggregate demand would remain at AD1
D. Demand would remain at AD1 and aggregate supply would remain at AS1