If a firm can change market prices by altering its output, then it
A. Engages in marginal cost pricing.
B. Is a price taker.
C. Faces a flat demand curve.
D. Has market power.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
By specializing and trading, a country is able to
A) produce but not to consume combinations of goods that lie beyond its production possibilities frontier. B) consume but not to produce combinations of goods that lie beyond its production possibilities frontier. C) obtain the absolute advantage in the goods it produces. D) both produce and consume combinations of goods that lie beyond its production possibilities frontier. E) neither produce nor consume combinations of goods that lie beyond its production possibilities frontier.
How does an increase in real GDP affect the demand for money curve?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the accompanying figure, which shows the market for cups of coffee. At the original market equilibrium: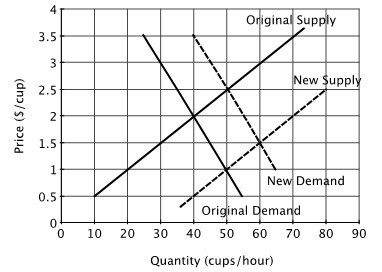
A. 60 cups are sold per hour at a price of $1.50 each. B. 50 cups are sold per hour at a price of $2.50 each. C. 50 cups are sold per hour at a price of $1.00 each. D. 40 cups are sold per hour at a price of $2.00 each.
Suppose that when disposable income increases by $1,000, consumption spending increases by $750. Given this information, we know that the marginal propensity to save (MPS) is
A. 1.33. B. 4. C. 0.75. D. 0.25.