Rutherford's scattering equation question
Scattering one unknown particle of Z1 off of another, much more massive target particle of Z2, you observe a certain number of particles scattered at an angle (your detector is of width
(your detector is of width 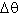 , at an angle
, at an angle from the beam axis, centered at an angle
from the beam axis, centered at an angle 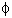 around the beam axis). Use Rutherford's scattering equation (and assumptions) to determine which of the following changes to the experiment would be most likely to increase the number of particles you detect with your detector.
around the beam axis). Use Rutherford's scattering equation (and assumptions) to determine which of the following changes to the experiment would be most likely to increase the number of particles you detect with your detector.
increase the velocity of the scattering particles.
a. increase the angle 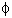 around the beam axis.
around the beam axis.
b. increase the cross section of the target nuclei.
c. increase the number of neutrons in the scattering nuclei.
d. increase the number of electrons in the target nuclei.
C.
Increasing the probability of the target nucleus scattering the scattering particle would be most likely to increase the number of particles detected at a certain angle.
You might also like to view...
An automobile is moving on a highway at 100 km/hr. Estimate the heat loss per unit area from the auto’s roof, which is at 30ºC, if the air temperature is 15ºC.
What will be an ideal response?
What other information do we combine with the luminosity of a Type Ia supernova to measure its distance?
A: energy. B: apparent brightness. C: temperature. D: size. E: redshift.
In a section of horizontal pipe with a diameter of 3.00 cm the pressure is 5.21 kPa and water is flowing with a speed of 1.50 m/s. The pipe narrows to 2.50 cm. What is the pressure in the narrower region?
A) 4.00 kPa B) 7.50 kPa C) 5.82 kPa D) 6.42 kPa E) 4.61 kPa
What do we mean by the interstellar medium?
A) the gas and dust that lies in between the stars in the Milky Way galaxy B) the dust that fills the halo of the Milky Way galaxy C) the middle section of the Milky Way galaxy D) the name of an oracle who can channel messages from beings that live near the star called Vega