What happened to the demand curve in the global cement market when China experienced a construction boom starting in 2004?
What will be an ideal response?
The demand curve shifted to the right after China entered the market, causing higher prices and higher quantities. China had a tremendous amount of construction projects to complete as a result of a growing economy. These projects required cement, and a lot of it, which caused the global quantity demanded to rise at any price.
You might also like to view...
Total government expenditure as a percentage of GDP is lower in the United States than in Sweden
a. True b. False
The Green Chemistry Program
a. calls for participants in the product cycle to reduce life cycle environmental effects of products b. is synonymous with product stewardship c. involves only participants from the scientific community d. involves partnerships with many sectors, including academia, industry, research centers, and others
In the figure below, AB is the production-possibility curve of Canada. The line PQ shows the price ratio of one bushel of wheat/bale of cotton. I1 and I2 are two of the community indifference curves of Canada. With free trade, Canada can achieve a level of well-being corresponding to I2. In the absence of international trade, one bushel of wheat will exchange for ________ bale(s) of cotton in Canada. After Canada engages in international trade, one bushel of wheat will exchange for ________ bale(s) of cotton.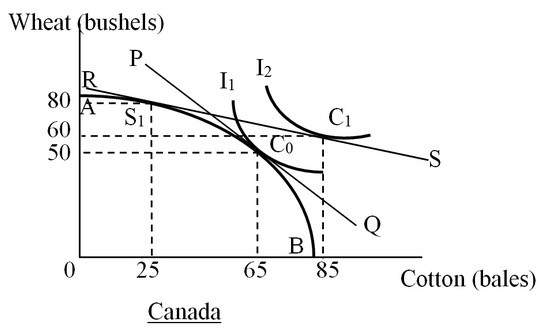
A. 65, 85 B. four; one C. one; 0.25 D. one; four
Both collusive and noncollusive oligopoly models suggest that price changes will be relatively infrequent in these types of industries.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)