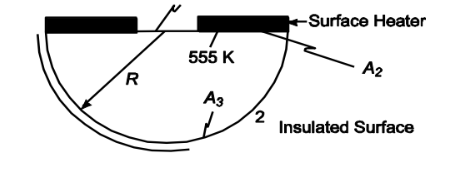
A radiation source is to be built, as shown in the diagram, for an experimental study of radiation. The base of the hemisphere is to be covered by a circular plate having a centered hole of radius R/2. The underside of the plate is to be held at 555 K by heaters embedded in its surface. The heater surface is back. The hemispherical surface is well-insulated on the outside. Assume gray diffuse processes and uniform distribution of radiation. (a) Find the ratio of the radiant intensity at the opening to the intensity of emission at the surface of the heated plate. (b) Find the radiant energy loss through the opening in watts for R = 0.3 m. (c) Find the temperature of the hemispherical surface.
GIVEN
• A radiation source as shown above
• Radius of hole = R/2
• Temperature of underside of plate (T2) = 555 K
• Underside of plate is black
• Hemispherical surface is well insulated on the outside
FIND
(a) The ratio of the radiant intensity at the opening to the intensity at the surface of the heated plate (G1/ Eb2)
(b) The radiant energy loss through the opening (q1) in watts for R = 0.3 m
(c) The temperature of the hemispherical surface (T3)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Gray diffuse processes
• Uniform distribution of radiation
• Radiation entering A1 is negligible, i.e., A1 as a black body at 0 K Heat loss through insulation is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
The problem consists of radiative exchange between two black surfaces and a gray surface. It can be solved by simplifying which applies to gray surfaces
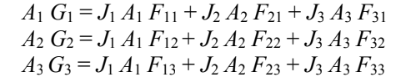
The radiosities, are
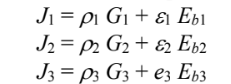
Let the opening the surface 1, the heater surface be surface 2, and the hemisphere be surface 3. Since A1 and A2 cannot see themselves or each other: F11 = F22 = F12 = F21 = 0 Since A1 and A2 are black ?1 = ?2 = 1 and ?1 = ?2 = 0 Neglecting radiation entering A1 Eb1 = 0 ? J1 = 0
In steady state, surface A3 has no net heat gain or loss q3 = 0.
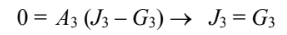
Incorporating these simplifications into the above equations
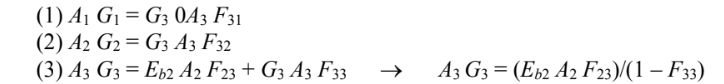
(a) Combining
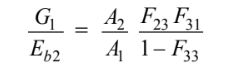
The shape factors must sum to unity: F31 + F32 + F33 = 1
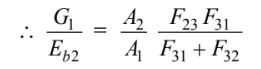
From examination of the geometry, it is clear that F13 = 1 and F23 = 1
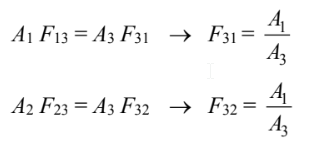
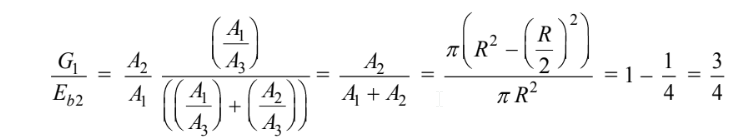
(b) The radiation energy loss at the opening is given by the irradiance of surface 1
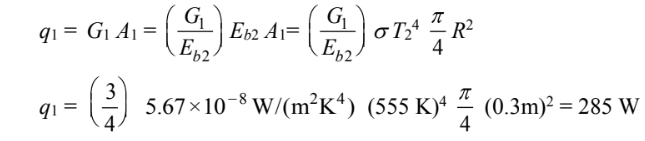
(c)
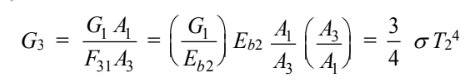
Since J3 = G3, yields
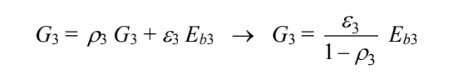
But A3 is opaque, so ?3 = 0
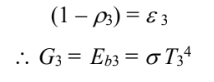
Combining these two equations
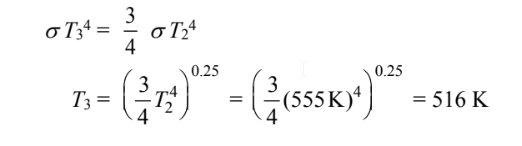
You might also like to view...
What are the three periods of Mars's planetary history?
What will be an ideal response?
The last page of a book is numbered 814 and the book is 3.00 cm thick. What is the average thickness of each page?
a. 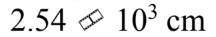
b. 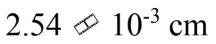
c. 
d. 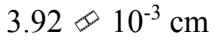
How is the refractive power, P, of a lens related to its focal length, f?
A. P = f B. P = 1/f C. P = 2*f D. P = f2
A cylindrical insulated wire of diameter 5.0 mm is tightly wound 200 times around a cylindrical core to form a solenoid with adjacent coils touching each other
When a 0.10 A current is sent through the wire, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field on the axis of the solenoid near its center? (?0 = 4? × 10-7 T • m/A) A) 6.6 × 10-5 T B) 2.5 × 10-5 T C) 1.3 × 10-5 T D) 3.6 × 10-5 T E) 9.8 × 10-5 T