Using Green's Theorem, compute the counterclockwise circulation of F around the closed curve C.F = - 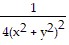 i; C is the region defined by the polar coordinate inequalities 1 ? r ? 2 and
i; C is the region defined by the polar coordinate inequalities 1 ? r ? 2 and 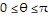
A. 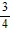
B. 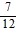
C. - 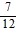
D. 0
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Find f(x) and g(x) such that h(x) = (f ? g)(x).h(x) = 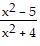
A. f(x) = 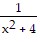 , g(x) = x2 - 5
, g(x) = x2 - 5
B. f(x) = 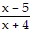 , g(x) = x2
, g(x) = x2
C. f(x) = x2 + 4, g(x) = x2 - 5
D. f(x) = x2, g(x) = 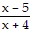
Multiply.(3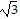 + 5
+ 5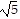 )2
)2
A. 152 + 15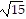
B. 152 + 30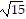
C. 34 + 30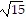
D. 152
Use calculus to find any critical points and inflection points of the given function. Then determine the concavity of the function and the intervals over which it is increasing/decreasing.f(x) = 6 - e-x
A. Critical points: critical point at x = 0 Inflection points: none Concavity: concave down for all real numbers Increasing: increasing for all x < 0 and decreasing for all x > 0 B. Critical points: none Inflection points: none Concavity: concave up for all real numbers Decreasing: decreasing for all real numbers C. Critical points: none Inflection points: point of inflection at x = 0 Concavity: concave down for all x < 0 and concave up for all x > 0 Increasing: increasing for all real numbers D. Critical points: none Inflection points: none Concavity: concave down for all real numbers Increasing: increasing for all real numbers
?Which property of determinants is illustrated by the equation 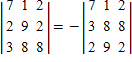
A. If two rows of a matrix are interchanged, the determinant of the matrix is multiplied by -1. B. If two columns of a matrix are interchanged, the determinant of the matrix is multiplied by -1. C. If a row of a matrix is subtracted from another row of the same matrix, the determinant of the matrix is multiplied by -1. D. If two matrices have any rows equal, the determinant of the matrix is multiplied by -1. E. If a column of a matrix is subtracted from another column, the determinant of the matrix is multiplied by -1.