What is the value of consumer surplus (CS) and producer surplus (PS) at equilibrium?
Consider the market for a Procter and Gamble biodegradable detergent. Suppose that market demand is QD = 120 – 3P, and market supply is QS = –50 + 2P, where P is the price per case and Q is the quantity in thousands per week.
CS is calculated as the area of the triangle between demand and the market price, and PS is the area of the triangle between supply and the market price. Sketching a graph makes the calculation more apparent, as shown below. Note that when labeling vertical intercepts for the supply and demand equations, it is easier to first write each equation in inverse form, i.e., P = f(Q). In this case, the inverse demand equation is P = 40 – ?QD and the inverse supply equation is P = 25 + ½ QS.
See graph below.
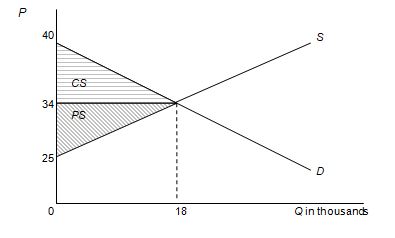
Now, it‘s a simple matter to calculate the areas of each triangle.
CS = ½ * base * height = ½ * 18 * 6 = $54 thousand
PS = ½ * base * height = ½ * 18 * 9 = $81 thousand
You might also like to view...
Suppose that Congress allocates $1 billion to clean up after hurricanes in 2016. It also raises taxes by $1 billion to keep the deficit from growing. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.9, what is the effect on equilibrium GDP?
A) GDP increases by $900,000. B) GDP increases by $10 billion. C) GDP increases by $1 billion. D) GDP does not change.
Assume that you allocate your income to calzones and juice and that you have not yet spent your entire budget. If the marginal utility of a fourth calzone is 100 and the marginal utility of a third glass of juice is 50, you would
a. eat a fourth calzone because it has higher marginal utility b. drink a third glass of juice c. drink a third glass of juice if its price is lower than the price of calzones d. drink a third glass of juice if its price is less than half the price of the calzone e. drink a third glass of juice because it has lower marginal utility
Monopolists can achieve any level of profit they desire because they have unlimited market power
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Suppose that the market for labor is initially in equilibrium. An increase in immigration will cause the equilibrium wage
a. and the equilibrium quantity of labor to rise. b. and the equilibrium quantity of labor to fall. c. to rise and the equilibrium quantity of labor to fall. d. to fall and the equilibrium quantity of labor to rise.