Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity v2 = 2.1 m/s at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C?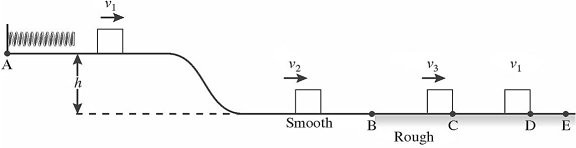
style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="148" width="576" />
A. -1.8 J
B. -3.6 J
C. -14 J
D. -6.4 J
E. -7.0 J
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A string on a guitar is stretched between two points 30.0 cm apart with a tension of 100 N. The mass/length of the string is 0.00300 kg/m. The velocity of wave propagation on the string is
A. 175 m/s. B. 183 m/s. C. 205 m/s. D. 267 m/s. E. 300 m/s.
Which planet has the highest average surface temperature and why?
A) Mercury, because it is closest to the Sun B) Mercury, because of its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere C) Venus, because of its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere D) Mars, because of its red color E) Jupiter, because it is so big
Under steady state conditions, a piece of wood 350 mm by 350 mm and 15 mm thick conducts heat through its thickness and loses no appreciable heat through its well-insulated sides
The rate of heat flow is measured to be 14.0 W when the temperature difference across its thickness is 28°C. Determine the thermal conductivity of this wood. A) 9.2 × 10-4 W/(m ? °C) B) 270 W/(m ? °C) C) 16 W/(m ? °C) D) 0.061 W/(m ? °C) E) 33 W/(m ? °C)
A 2.0-mol ideal gas system is maintained at a constant volume of 4.0 L. If 100 J of heat is added, what is the work done on the system?
a. zero b. 5 J c. ?3.3 J d. 20 J e. 3.3 J