Government decisions tend to be biased toward actions that have
a. current costs and future benefits that are both easily observable.
b. future costs that are difficult to identify and current benefits that are easily observable.
c. future costs and future benefits that are both difficult to identify.
d. current costs that are easily observable and future benefits that are difficult to identify.
B
You might also like to view...
Assume that goods X and Y are substitutes and are produced in perfectly competitive markets. All else constant, in the short run, a decrease in the supply of good X would cause:
A) an increase in the demand for good Y. B) a decrease in the demand for good Y. C) an increase in the supply of good Y. D) a decrease in supply of good Y.
Figure 5-9
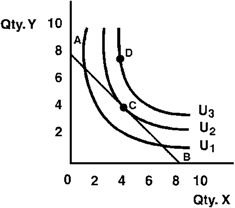
In Figure 5-9, the consumer's marginal rate of substitution at his optimum choice of X and Y is
a.
?1.
b.
16.
c.
8.
d.
?8.
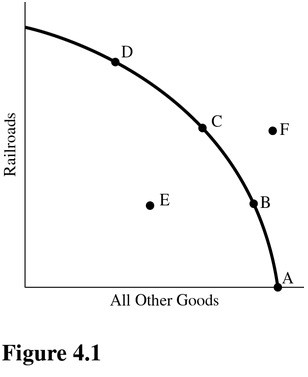 Using Figure 4.1, suppose that point B represents the optimal mix of output for a society. If market forces cause society to produce and consume at point C, then
Using Figure 4.1, suppose that point B represents the optimal mix of output for a society. If market forces cause society to produce and consume at point C, then
A. There is market failure. B. Points A and D are unattainable with the given resources and technology. C. The forces of supply and demand will return society to point B. D. There is government failure.
Lowering taxes is a contractionary Keynesian policy.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)