Explain the process through which kinetic energy is conserved in an elastic collision
What will be an ideal response?
If the two objects are very hard and no heat or other form of energy is produced in the collision, then the kinetic energy of the two objects is the same after the collision as before. For the brief moment during which the two objects are in contact, some (or all( of the energy is stored momentarily in the form of elastic potential energy. But if we compare the total kinetic energy just before the collision with the total kinetic energy just after the collision, and they are found to be the same, then we say that the total kinetic energy is conserved.
You might also like to view...
As the moon covers the solar disk during a solar eclipse, a flash spectrum of the sun's chromosphere can be recorded. This flash spectrum reveals an emission spectrum and provides information on the properties of the chromosphere. As the moon moves from the inner chromosphere to the outer chromosphere, the spectral lines present in the flash spectrum change. What is going on in the chromosphere
that produces the changes in the flash spectrum? I. The temperature of the chromosphere decreases as the distance from the photosphere increases. II. The temperature of the chromosphere increases as the distance from the photosphere increases. III. The density of the chromosphere decreases as the distance from the photosphere increases. IV. The density of the chromosphere increases as the distance from the photosphere increases. a. I & III b. I & IV c. II & III d. II & IV e. I
Radioactivity Basics: An oxygen-15 nucleus,  O, decays to another atomic nucleus by emitting a ?+ ray. What is the other atomic nucleus?
O, decays to another atomic nucleus by emitting a ?+ ray. What is the other atomic nucleus?
A. 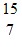 N
N
B. 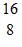 F
F
C. 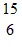 C
C
D. 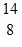 C
C
E. 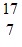 N
N
This figure shows the Cepheid period-luminosity relation. What is the approximate luminosity of a Cepheid star that varies in brightness with a period of 10 days?
A) about 1000 times the luminosity of the Sun B) about 3000 times the luminosity of the Sun C) about 10,000 times the luminosity of the Sun D) about 30,000 times the luminosity of the Sun
The principle of equivalence states that
A) the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. B) the speed of light is the same in any frame of reference. C) clocks that move relative to one another keep time at different rates. D) the length of an object depends on its speed relative to a given observer. E) all physical experiments conducted in a uniform gravitational field and in an accelerated frame of reference give identical results.