A spacecraft (mass = m) orbits a planet (mass = M) in a circular orbit (radius = R). What is the minimum energy required to send this spacecraft to a distant point in space where the gravitational force on the spacecraft by the planet is negligible?
a. GmM/(4R)
b. GmM/R
c. GmM/(2R)
d. GmM/(3R)
e. 2GmM/(5R)
c
You might also like to view...
Newtonian physics tells us that Kepler's second law is a result of the conservation of ____
a. angular momentum b. linear acceleration c. energy d. mass e. velocity
Characteristics of Waves: What is the wavelength of the wave shown in the figure?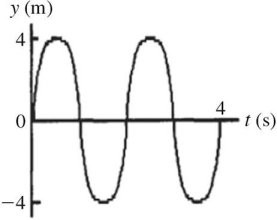
A. 8 m. B. 4 m. C. 2 m. D. 1 m. E. It cannot be determined from the given information.
Rank the five terrestrial worlds in order of size from smallest to largest
A) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Moon, Mars B) Mercury, Moon, Venus, Earth, Mars C) Moon, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars D) Moon, Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth E) Mercury, Moon, Mars, Earth, Venus
What is the primary basis upon which we divide the ingredients of the solar nebula into four categories (hydrogen/helium; hydrogen compound; rock; metal)?
A) the temperatures at which various materials will condense from gaseous form to solid form B) the locations of various materials in the solar nebula C) the atomic mass numbers of various materials D) the amounts of energy required to ionize various materials