A) Sam pays $600 for 30 days of guitar classes. He attends an hour-long class every day. If, instead of attending class, he works at a part-time job, he would be paid $5 an hour. Or, he could work at a fast-food outlet and earn $9 per hour
Once he has already paid a nonrefundable fee of $600 to enroll in the class, what is his opportunity cost of attending each hour of class?
b) Suppose workers decide to work more and consume less leisure when their hourly wage rate increases. What could explain this behavior?
a) Sam's opportunity cost will measure the next best use of an hour of his time plus the hourly cost of guitar classes. Once he pays the nonrefundable $600, there is no other cost other than the value of his time. With an hour of time, he has two options: work for $5 per hour, or work for $9 per hour. Therefore, the next best use of an hour that Sam spends on guitar classes is equal to the $9 he could have earned per hour by working at the fast-food outlet. Sam's opportunity cost of attending his guitar classes is $9 per hour.
b) With an increase in their hourly wage rates, workers work more and consume less leisure due to a change in their opportunity cost. Assuming that the initial wage of an employee is $10 per hour, the opportunity cost of one hour of rest or leisure is $10 per hour. Now, if the wage rate increases from $10 to $20 per hour, the opportunity cost of one hour of rest or leisure also increases to $20 per hour. Therefore, taking an hour of rest becomes more expensive for employees and they tend to work more than they used to.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below where the nominal interest rate equals 6% and the money supply equals 600. If the Federal Reserve wants to raise the interest rate to 8%, it must ________ the money supply to ________. 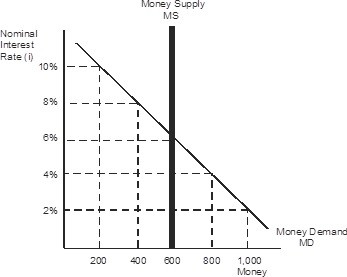
A. increase; 400 B. decrease; 400 C. increase; 800 D. decrease; 800
For this tax schedule, what is the marginal tax rate for an individual with taxable income of $49,000?
a. 0% b. 10% c. 25% d. 35%
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market with free entry and exit, firms operate at their __________ scale
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The following is the set of conditions is necessary for ________ for a perfectly competitive firm: P = SRMC = SRAC = LRAC.
A. long-run production with economic losses B. long-run equilibrium C. short-run shut down D. long-run profit