How does gravity lensing let us find massive dark objects?
What will be an ideal response?
When a black hole or brown dwarf passes between us and a bright star, the gravity of the dark object can bend and focus the light of the distant star, making it brighten temporarily. The more massive the unseen object, the longer this brightening will last.
You might also like to view...
A projectile is projected from the origin with a velocity of 45.0 m/s at an angle of 30.0 degrees above the horizontal. What is the velocity when the projectile hits the ground?
A. Vx = 35.7 m/s, Vy = -22.5 m/s B. Vx = 39.0 m/s, Vy = -22.5 m/s C. Vx = 35.7 m/s, Vy = -39.0 m/s D. Vx = 39.0 m/s, Vy = -35.7 m/s E. Vx = 22.5 m/s, Vy = -22.5 m/s
A ball is tossed upward. Neglecting air drag, the acceleration along its path is
A) 0 g. B) g downward. C) g upward. D) g upward, then g downward. E) none of the above
An constant electric field, 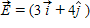
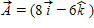
src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Chapter_25_Gauss_apos_s_Law.__media__7d94a3f5-3b36-4dc7-aedd-c86064e2bc84.PNG" style="vertical-align:middle;" />. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through this area? A. 24 N ? m2/C B. 48 N ? m2/C C. 0.24 N ? m2/C D. 0.48 N ? m2/C E. 0
A child on a sled starts from rest at the top of a 15° slope. If the trip to the bottom takes 15.2 s, how long is the slope? Assume that frictional forces may be neglected
A) 293 m B) 586 m C) 1130 m D) 147 m