A medical test has been designed to detect the presence of a certain disease. Among those who have the disease, the probability that the disease will be detected by the test is 0.91. However, the probability that the test will erroneously indicate the presence of the disease in those who do not actually have it is 0.02. It is estimated that 2% of the population who take this test have the disease.
If an individual takes the test twice and both times the test is positive, what is the probability that the person actually has
the disease?
a. 0.481
b. 0.980
c. 0.023
d. 0.519
e. 0.977
e. 0.977
You might also like to view...
Determine whether f is a linear function. If f is linear, give the values for m and b so that f may be expressed as 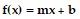 .f(x) = -12x
.f(x) = -12x
A. Linear; m = - 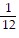 , b = 0
, b = 0
B. Linear; m = 12, b = 1
C. Linear; m = -12, b = 0
D. Nonlinear
Use a proportion to solve the problem.A building casts a shadow 39 m long. At the same time, the shadow cast by a 41-cm tall pole is 53 cm long. Find the height of the building. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a meter.
A. 48.9 m B. 50.4 m C. 28.7 m D. 30.2 m
Solve the problem.In Antarctica, the high temperatures for the last four days have been 17.2°F, 5.6°F, 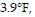 and
and 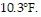 What is the average high temperature for this
What is the average high temperature for this  period?
period?
A. 8.65°F B. 9.25°F C. 9.9°F D. 7.27°F
Solve the linear inequality. Express the solution in set-builder notation.-4(2x + 12) < -12x - 36
A. {x|x > 3} B. {x|x > -12} C. {x|x < -12} D. {x|x < 3}