Suppose a family is holding $1000 in its checking account for normal transactions, $500 in cash for emergencies, and $1500 as a store of value when the interest rate is 4 percent
If the interest rate rises to 10 percent, which of the following patterns of holding money would be most likely and why? A) Transactions demand—$1000; Precautionary demand—$350; Asset demand—$500, because the opportunity cost of holding money has increased. The reduction money balances held as an asset is greatest because interest-bearing assets are much more attractive when interest rates are higher.
B) Transactions demand—$500; Precautionary demand—$500; Asset demand—$1400, because the opportunity cost of holding money balances has risen. The reduction in money balances held for transaction purposes falls the most because people start using credit cards more when the opportunity cost of holding money increases.
C) Transactions demand—$1000; Precautionary demand—$500; Asset demand—$500, because only the asset demand is responsive to changes in the interest rate.
D) Transactions demand—$800; Precautionary demand—$600; Asset demand—$1500, because people can economize on their money balances for making transactions, but the possibility of an emergency increases with the interest rate. People will also expect rates to go higher, so they will hold money as an asset until the rates increase further.
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is associated with a less elastic demand curve?
a. availability of many close substitutes b. a greater amount of time for consumers to respond to a price change c. a smaller percentage of income spent on the good in question d. all of the above
The process of building up capital includes
a. acquiring funds from banks and other sources. b. use of borrowed funds to hire inputs to build factories, warehouses, etc. c. completion of the investment process by adding machinery and inventory. d. All of the above are correct.
A monopolistically competitive firm earning profits in the short run will find the demand for its product decreasing and becoming more elastic in the long run as new firms move into the industry until
A) the original firm is driven into bankruptcy. B) the firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic. C) the firm's demand curve is tangent to its average total cost curve. D) the firm exits the market.
In the diagram, a shift from AS 2 to AS 3 might be caused by a(n):
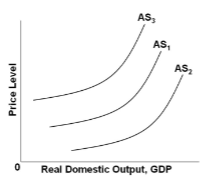
A. decrease in interest rates.
B. increase in business taxes and costly government regulation.
C. decrease in the prices of domestic resources.
D. decrease in the price level.