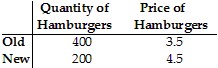 Table 5.1Refer to Table 5.1. A change in the price of hamburgers caused the change in quantity demanded shown in the table. The price elasticity of demand for hamburgers (calculated using the initial value formula) is:
Table 5.1Refer to Table 5.1. A change in the price of hamburgers caused the change in quantity demanded shown in the table. The price elasticity of demand for hamburgers (calculated using the initial value formula) is:
A. 0.25.
B. 0.50.
C. 1.
D. 1.75.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If a good has an absolute price elasticity of 0, the demand for the good is
A) unit elastic. B) inelastic. C) perfectly inelastic. D) elastic.
How would a decrease in the price of the feed grains used to feed cattle affect the market for beef?
a. The demand for beef would increase, increasing beef prices. b. The demand for beef would decrease, decreasing beef prices. c. The supply of beef would increase, decreasing beef prices. d. The supply of beef would decrease, increasing beef prices.
"Politics is too often the thing that gets in the way of good economic policy being implemented." The economist who said this most likely
A) believes that fiscal policy is preferable to monetary policy when it comes to stabilizing the economy. B) prefers discretionary monetary policy to rule-based monetary policy. C) believes that there will be a lot of crowding out if government spending is increased. D) prefers rule-based monetary policy to discretionary monetary policy.
The elasticity of labor supply:
A. for a town should equal the elasticity of labor supply for a state. B. should be greater for a state than for a town because people can travel more easily between states than between towns. C. should be greater for a town than for a state because people are more likely to consider work in a neighboring town than in another state. D. for a town is not related to the elasticity of labor supply for a state.