A unified model of active galaxy cores can explain different types of Seyfert galaxies, quasars and other active galaxy types by differences in the ____
a. mass of the supermassive black hole
b. size and thickness of the accretion disk
c. magnetic flux strength in the jets
d. amount of dust in the accretion disk
e. tilt of the accretion disk to the line of sight
e
You might also like to view...
From hottest to coolest, the order of the spectral types of stars is
A) OBAFGKM. B) OBAGFKM. C) ABFGKMO. D) OMKGFBA. E) ABCDEFG.
A horizontal force of 40 N pushes an object of mass 5.0 kg up an inclined plane through a distance of 1.6 m measured along the plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. Neglect friction and use g = 10 m/s2
(a) What is the work done by the horizontal force on the object? (b) What is the work done by the net force on the object? (c) What is the work done by the normal force on the object?
Which of the following statements is true in the context of radioactive elements?
A) The abundances of the daughter isotopes of radioactive elements in a rock gradually decrease. B) The abundance of a radioactive element in a rock gradually decreases. C) Uranium-238 has the longest half-life among all the other radioactive substances. D) Potassium-40 has the longest half-life among all the other radioactive substances.
Given the equations below, which description best fits the physical situation? 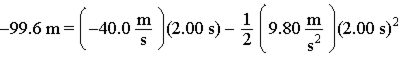
A. A projectile's displacement two seconds after being fired downward with a speed of 30.0 m/s. B. A projectile's displacement two seconds after being fired downward with a speed of 40.0 m/s. C. A projectile's displacement two seconds after being fired downward with a speed of 50.0 m/s. D. A projectile's displacement two seconds after being fired downward with a speed of 60.0 m/s. E. A projectile's displacement two seconds after being fired downward with a speed of 80.0 m/s.