A student set up an experiment to test if plants give off water vapor. Fifty pea plants, growing in pots, were covered with individual glass containers and left overnight. The next morning, the inside of each lid was covered in droplets of water. The lab student concluded that plants generally give off water vapor. What critique would you make of the experimental design?
A. There was no control so the water could have come from other sources such as air in the jar or the
soil.
B. There was not a large enough sample of pea plants used to get adequate data.
C. The student did not have a clearly stated hypothesis before beginning the experiment.
D. The experiment was not precise, meaning it was not reproducible.
Clarify Question
1. What is the key concept addressed by the question?
2. What type of thinking is required?
3. What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
1. What do you know about experimental design? How does it relate to the question?
Consider Possibilities
1. What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
2. What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
1. Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
1. Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
A. There was no control so the water could have come from other sources such as air in the jar or the
soil.
Clarify Question
1. The question is about designing an experiment.
2. This question is asking to analyze the design of an experiment.
3. The hypothesis is that plants give off water vapor.
50 pots each containing plants were covered with lids.
The next day each pot contained water vapor.
Gather Content
1. The weakness of
this experiment is that it does not contain a control group, so you cannot conclude that the water came from the plants or from the soil or other components of the experiment.
Consider Possibilities
1. 50 plants is a large sample size, there was a hypothesis and the experiment was carried out correctly.
2. So you can eliminate these as answers.
Choose Answer
1. The best answer is that there was not an appropriate control group. Half of the pots should have been prepared with no plants in them to be sure the water vapor was not coming
from the soil or pots.
Reflect on Process
1. This question asked you to apply the definitions of deductive and inductive reasoning to specific
examples. If you got the correct answer, great job! If you got an incorrect answer, where did the process break down? Did you not realize that all of the pots contained a plant? While the hypothesis was not clearly stated, you could infer it from the first sentence of the problem. Did you think that 50 plants was too small a sample?
You might also like to view...
What is the p value from this test? (Pick the most accurate choice.)
In Drosophila, singed bristles (sn) and carnation eyes (car) are both caused by recessive X-linked alleles. The wild-type alleles (sn+ and car+) are responsible for straight bristles and red eyes, respectively. A sn car female is mated to a sn+car+ male and the F1 progeny are interbred. The F2 are distributed as follows:
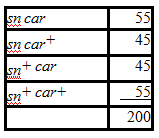
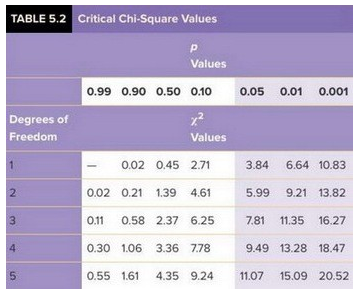
A) p> 0.5
B) 0.1
D) p< 0.05
E) p< 0.01
How are the four major types of biological molecules similar in structure?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer questions 62–66 in reference to the five nucleotides
listed below:a. guanine b. cytosine c. pyrimidine d. thymine e. uracil M 62. Erwin Chargaff’s data indicates that within a species the amount of adenine is always equal to the amount of this. E 63. This nucleotide is not incorporated into the structure of the DNA helix. D 64. This nucleotide is a double-ring molecule. M 65. If one chain of a DNA molecule has a purine at a given position, this complements it on the other chain. D 66. Two hydrogen bonds connect adenine to __________ in the DNA molecule.
Which of the following would NOT be an action of the complement system?
a. lysis of a pathogen's membrane b. trapping of pathogens in tangled protein threads c. marking of pathogens for destruction by macrophages d. attraction of phagocytes to the scene of pathogen invasion e. membrane attack complexes