Describe the thermal production of charge carriers in a semiconductor and how this process limits the operation of a semiconductor device.
What will be an ideal response?
Analysis:
At a temperature of absolute zero, ALL valence electrons in a semiconductor are contained in a covalent bond and there are NO charge carriers.
The internal or thermal energy of a solid material is caused by the vibration of the atoms and electrons about their equilibrium position. As the temperature of the material increases, its thermal vibrational energy increases. Some electrons will gain sufficient energy to escape the covalent bond in the valence band, and "jump" past the energy gap into the conduction band. As a consequence, TWO charge carriers are generated. The conduction or free electron in the conduction band is a negative charge carrier. The vacancy in the valence band covalent bond or "hole" is a positive charge carrier.
A conduction band electron may also give up energy and recombine with a valence band hole.
The generation and recombination rates both increase with temperature. At any particular temperature, they are equal and produce equal equilibrium densities of electrons and holes. The equilibrium carrier densities increase with temperature. For Silicon at T = 300 K [approximately room temperature]:
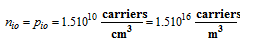
[A number of carriers is a dimensionless quantity and may be omitted from the units.]
Almost all semiconductors devices are "doped" to achieve DIFFERENT densities of positive and negative carriers. A "P-type" semiconductor has a higher density of positive carriers and an "N-type" semiconductor has a higher density of negative carriers. However, at high temperatures the density of thermally produced carriers becomes very large and significantly reduces or nullifies the effects of the doping, i.e., the positive and negative carrier densities become nearly equal. For this reason, semiconductor devices cannot be used in high temperature applications. The limit in temperature depends on the semiconductor material.
You might also like to view...
Rear brakes do less work during hard braking than the front brakes because ________
A) The rear brakes are larger B) The rear tires have less traction C) The vehicle weight transfers forward D) Both B and C are correct
Which single-phase AC motor contains a start winding, run winding, and a centrifugal switch?
A. repulsion-start/induction-run B. capacitor run C. split-phase D. universal
As clutch friction facings wear on a truck pull-type clutch, how is clutch pedal free travel affected?
A. decreases B. increases C. unaffected
When a circuit has only one path, the _____ is the same at any point.
A. voltage B. current C. power D. resistance