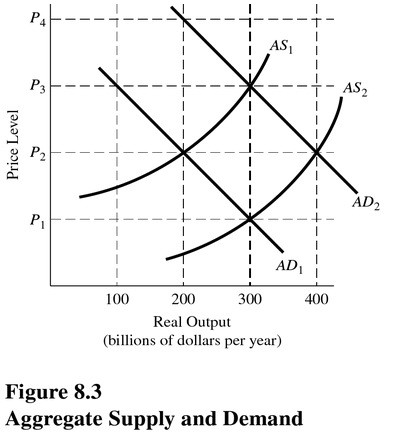
 Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1. Which curve would have shifted, and in what direction would it have shifted, if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1. Which curve would have shifted, and in what direction would it have shifted, if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
A. Aggregate demand would have shifted to the left.
B. Aggregate supply would have shifted to the right.
C. Aggregate demand would have shifted to the right.
D. Aggregate supply would have shifted to the left.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Regarding price leadership, which of the following is NOT true?
a. one firm may establish itself as the dominant firm b. the dominant firm is frequently a larger size or has lower cost structure c. Price leadership is a model of price-output determination d. Once established, a barometric price leader will not change e. price leadership is a pricing strategy followed in many oligopolistic industries
When comparing the Keynesian and monetarist approaches, the only substantive difference is that
a. the Keynesian equation leads to a prediction of real GDP; the monetarist equation leads to a prediction of nominal GDP. b. Keynesians concentrate on aggregate demand and monetarists concentrate on aggregate supply. c. Keynesians approach aggregate demand by multiplying the money supply by velocity, while monetarists use the equilibrium conditions of the expenditure schedule. d. Keynesian analysis suggests that money affects consumption first while monetarist analysis suggests that money affects investment spending first.
An increase in the money supply
a. lowers the interest rate, causing a decrease in investment and an increase in GDP. b. lowers the interest rate, causing an increase in investment and a decrease in GDP. c. lowers the interest rate, causing an increase in investment and an increase in GDP. d. raises the interest rate, causing an increase in investment and an increase in GDP. e. raises the interest rate, causing a decrease in investment and a decrease in GDP.
The term "growing income inequality" implies that the:
A. poor are getting poorer in both a relative and an absolute sense. B. Lorenz curve is shifting toward the diagonal. C. diagonal is shifting toward the Lorenz curve. D. upper quintiles of income receivers are getting relatively more of the total income than