Using Figure 2 below, suppose that the economy started at PAE2. A potential change that could cause the economy to go from PAE2 to PAE1 might be:

A. consumption increases.
B. investment increases.
C. export increase.
D. government spending decreases.
D. government spending decreases.
You might also like to view...
The nominal interest rate ________
A) makes no allowance for inflation B) is a percentage of the amount borrowed C) is the rate that most banks advertise D) all of the above E) none of the above
Use the aggregate expenditures model and assume the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is 0.80 . A decrease in government spending of $1 billion would result in a decrease in GDP of:
a. $0. b. $0.8 billion. c. $1.0 billion. d. $5.0 billion. e. $8.0 billion.
The change in aggregate demand that results from fiscal expansion changing the interest rate is called the
a. multiplier effect. b. crowding-out effect. c. accelerator effect. d. Ricardian equivalence effect.
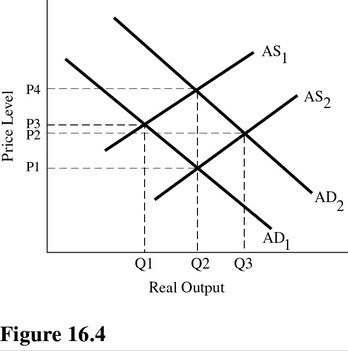 Refer to Figure 16.4. If the economy is initially in equilibrium at P3 and Q1, which of the following policies would move the economy to equilibrium at P2 and Q3?
Refer to Figure 16.4. If the economy is initially in equilibrium at P3 and Q1, which of the following policies would move the economy to equilibrium at P2 and Q3?
A. Restrictive supply-side policy alone. B. A combination of restrictive fiscal policy and restrictive monetary policy. C. A combination of expansionary monetary policy and expansionary supply-side policy. D. Contractionary monetary policy alone.