Energy Conservation With Conservative Forces: Swimmers at a water park have a choice of two frictionless water slides, as shown in the figure. Although both slides drop over the same height h, slide 1 is straight while slide 2 is curved, dropping quickly at first and then leveling out. How does the speed v1 of a swimmer reaching the bottom of slide 1 compare with v2, the speed of a swimmer reaching the end of slide 2?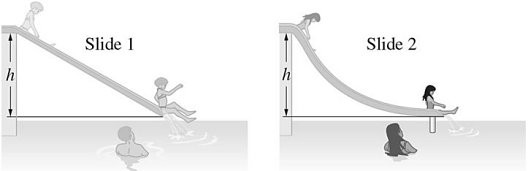
A. v1 > v2
B. v1 < v2
C. v1 = v2
D. The heavier swimmer will have a greater speed than the lighter swimmer, no matter which slide he uses.
E. No simple relationship exists between v1 and v2.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Energy Conservation With Conservative Forces: In a museum exhibit of a simple pendulum, a very small but dense 6.0-kg ball swings from a very light 2.5-m wire. The ball is released from rest when the pendulum wire makes a 65° angle with the vertical, and it swings in a circular arc with no appreciable friction or air resistance. What is the tension in the wire just as the ball swings through its lowest position?
A. 11 N B. 59 N C. 68 N D. 130 N E. 0 N
Rotational Kinetic Energy: A string is wrapped tightly around a fixed frictionless pulley that has a moment of inertia of 0.0352 kg ? m2 and a radius of 12.5 cm. The string is pulled away from the pulley with a constant force of 5.00 N, causing the pulley to rotate. What is the speed of the string after it has unwound 1.25 m if the string does not slip on the pulley?
A. 2.09 m/s B. 2.36 m/s C. 1.18 m/s D. 3.18 m/s E. 4.95 m/s
In massive stars, three helium atoms fuse together, forming a carbon nucleus. This reaction heats the core of the star. The net mass of the three helium nuclei must therefore be
A) higher than that of the carbon nucleus. B) less than that of the carbon nucleus. C) the same as that of the carbon nucleus (mass is always conserved).
A superconducting wire carries a current of 104 A. Find the magnetic field at a distance of 0.25 m from the wire. (µ0 = 4p × 10^-7 T×m/A)
a. 1.6 × 10^-2 T c. 8 × 10^-3 T b. 2 × 10^-3 T d. 3.2 × 10^-2 T