Cardiac muscle cells obtain energy almost exclusively through
A) anaerobic pathways.
B) protein stores.
C) glycolysis.
D) aerobic respiration.
E) the Krebs cycle.
D) aerobic respiration.
You might also like to view...
Using the figure below, identify the location where each process occurs.
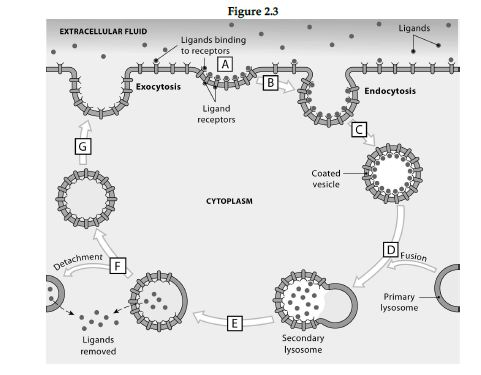
1 Pockets pinch off, forming endosomes known as coated vesicles.
2 Coated vesicles fuse with primary lysosomes to form secondary lysosomes.
3 Target molecules (ligands bind to receptors in plasmalemma.
4 The endosome fuses with the plasmalemma, and the receptors are again available for ligand binding.
5 The lysosomal and endosomal membranes separate.
6 Areas coated with ligands form deep pockets in plasmalemma surface.
7 Ligands are removed and absorbed into the cytoplasm.
The nucleus is an organelle enclosed in a double layer of membrane.
a. true b. false
The prominent indentation on the medial surface of the kidney is the
A) calyx. B) pelvis. C) ureter. D) hilum. E) pyramid.
The phase in the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles are completely closed and the volume of blood in them is constant is referred to as the
a. quiescent period. b. isovolumetric relaxation phase. c. ventricular ejection phase. d. isovolumetric contraction phase.