Find the binding energy per nucleon (in MeV/nucleon) of carbon-12. Assume: mC = 12.000 000 u m p = 1.007 825 u m n = 1.008 665 u u = 1.66 × 10^?27 kg
a. 1.2
b. 4.2 × 10^?2
c. 7.4
d. 7.7
e. 5.6
d
You might also like to view...
When a lump of uranium is broken into smaller pieces, the total surface area
A) decreases. B) remains the same. C) increases.
The highest high tides and the lowest low tides occur when the Moon is
A. full or new. B. full only. C. new only. D. first and third quarter.
When you double the number of windings in a solenoid keeping all other parameters (radius, length and current) fixed, the magnetic field at the center of the solenoid will
A) double. B) triple. C) quadruple. D) be reduced to one-fourth as much. E) be reduced to half as much.
Benzene flowing at 12.5 kg/s is to be cooled continuously from 80°C to 54°C by 10 kg/s of water available at 15.5°C. Using Table 10.6, estimate the surface area required for (a) cross-flow with six tube passes and one shell pass with neither of the fluids mixed and (b) a counterflow exchanger with one shell pass and eight tube passes with the colder fluid inside tubes.
GIVEN
• Benzene coded by water in a heat exchanger
• Benzene flow rate m b= 12.5 kg/s
• Water flow rate m w= 10 mg/s
• Benzene temperatures
? (Tb,in) = 82°C
? (Tb,out) = 54°C
• Water inlet temperature (Tw,in) = 15.5°C
FIND
The surface area required for (a) Cross-flow, 6 tube passes, 1 shell pass, both unmixed (b) Counterflow, 8 tube passes, 1 shell pass, water in tubes
SKETCH
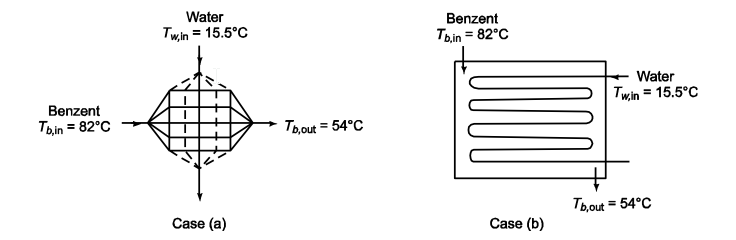
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the specific heat of water at 20°C (cpw) = 4182 J/(kg K)
the specific heat of Benzene at 68°C (cpb) = 1926 J/(kg K)