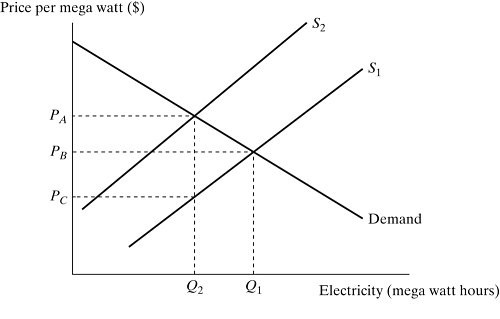
 Figure 9.9 depicts a market for electricity. S1 is the supply curve without the external costs. S2 is the supply curve with the $T tax. Assume electricity production incurs external costs. If the government imposes a pollution tax of $T per mega watt:
Figure 9.9 depicts a market for electricity. S1 is the supply curve without the external costs. S2 is the supply curve with the $T tax. Assume electricity production incurs external costs. If the government imposes a pollution tax of $T per mega watt:
A. the equilibrium price of electricity increases but the equilibrium output decreases.
B. the equilibrium price of electricity decreases but the equilibrium output increases.
C. both the equilibrium price and output increase.
D. both the equilibrium price and output decrease.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Steve is finding it impossible to get over his most recent break-up and finds himself talking about her constantly. An example of a commitment device that Steve could use to get over her would be:
A. to allow Steve's best friend to punch him in the arm any time he mentions her name. B. to take a cold shower every morning. C. to start dating someone else. D. None of these is a commitment device.
What portion of the demand curve will profit-maximizing monopolists choose to operate on: the inelastic portion or elastic portion? Why?
Most economic model builders would claim that their models
a. include all real-world economic activities b. portray how the real economy works c. take into account all the complexities of how people behave d. contradict the ceteris paribus assumption e. consider all the important pressing issues people confront
Why might an equation that has always predicted accurately in the past prove to be wrong following a policy change?
a. Because the policy may change people's behavior and invalidate the equation. b. Because people's expectations may cease to be rational. c. Because uncertainty means that every equation contains some degree of error. d. Because the policy change may affect economic variables not contained in the equation.