The mean free path of a molecule is  m in an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. What is the mean free path when the pressure of the gas is doubled and the temperature is tripled?
m in an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. What is the mean free path when the pressure of the gas is doubled and the temperature is tripled?
a. 
b. 
c. 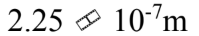
d. 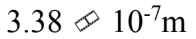
e. 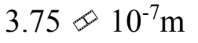
d. 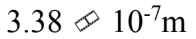
You might also like to view...
Which represents v vs. t for a ball which is thrown straight up, reaches the top, and falls back down (but before it hits the ground)?
A. 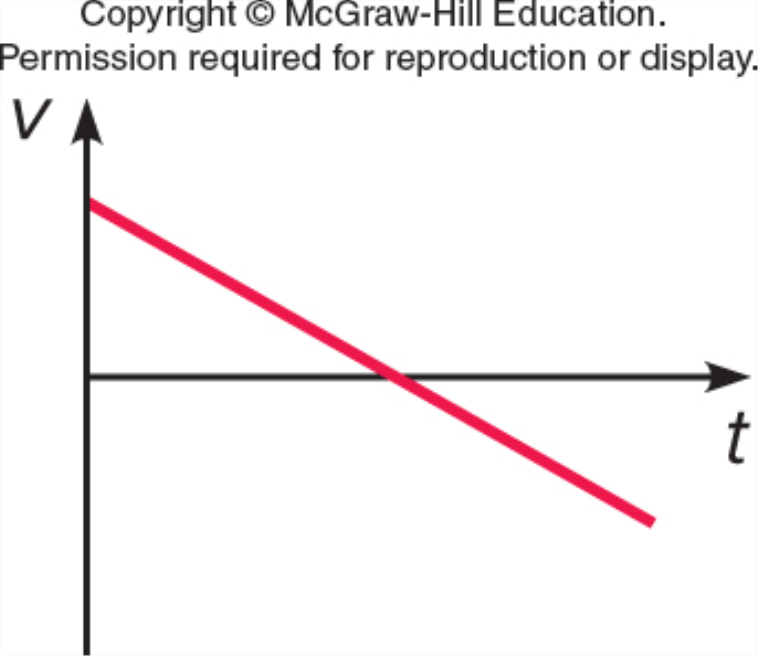
B. 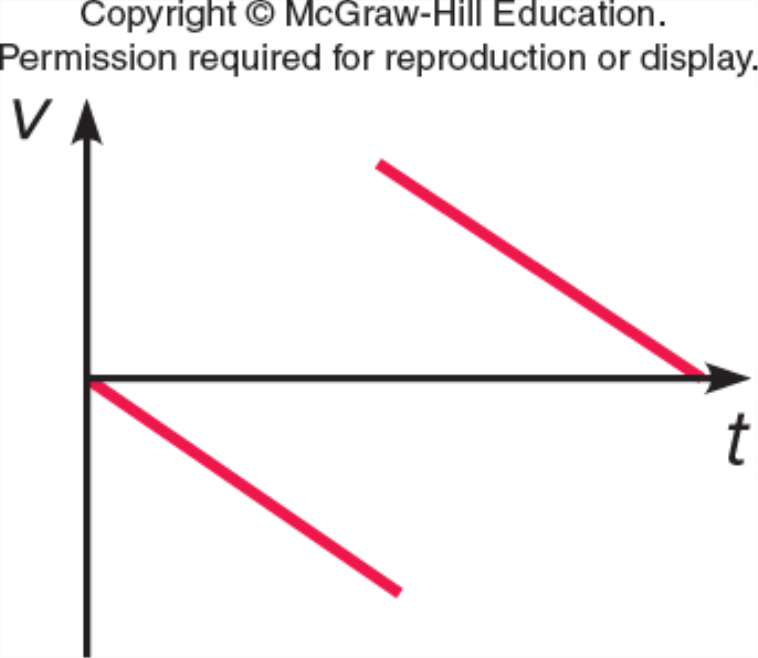
C. 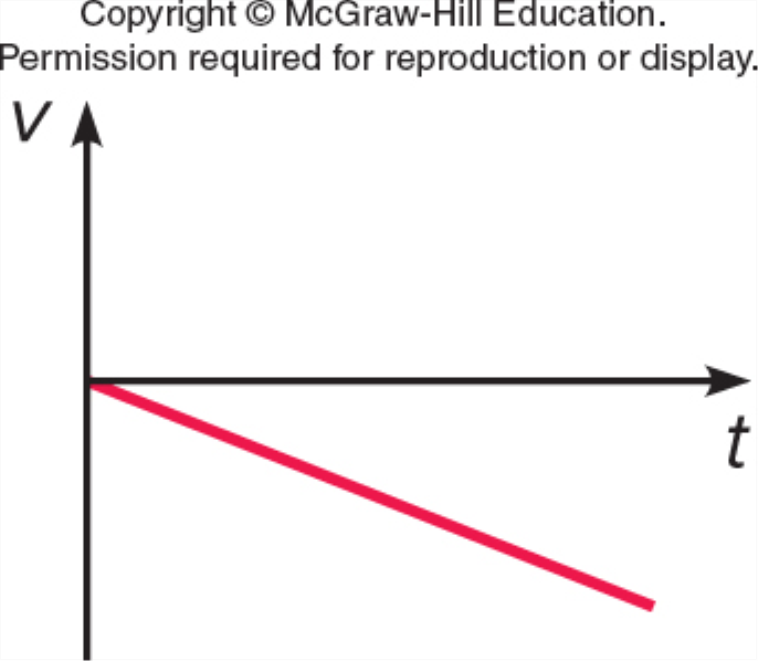
D. 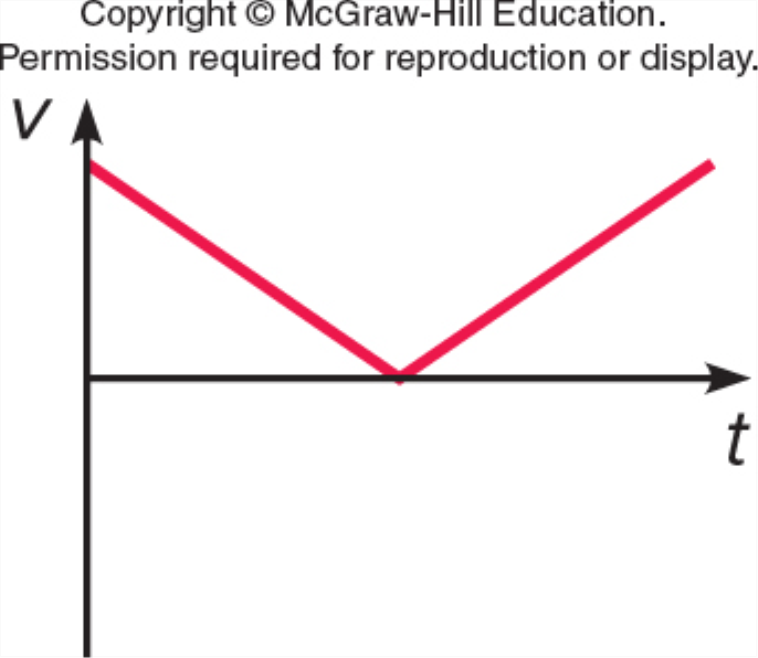
After landing on an unexplored Klingon planet, Spock tests for the direction of the magnetic field by firing a beam of electrons in various directions and by recording the following observations: Electrons moving upward feel a magnetic force in the
northwest direction. Electrons moving horizontally toward the north are pushed downward. Electrons moving horizontally toward the southeast are pushed upward. Mr. Spock therefore concludes that the magnetic field at this landing site is in which direction? A) toward the east B) toward the northeast C) toward the southwest D) toward the southeast E) toward the west
A container having a volume of 1.0 m3 holds 5.0 moles of helium gas at 50°C. If the helium behaves like an ideal gas, the total energy of the system is
a. 2.0 × 10^4 J. b. 2.5 × 10^4 J. c. 1.7 × 10^3 J. d. 1.5 × 10^3 J. e. 4.0 × 10^4 J.
What happens when the molecule-to-molecule attractions in the solute are comparable to those in the solvent?
A) The solute can have infinite solubility in the solvent. B) The solute does not dissolve in the solvent. C) The material has only limited solubility in the solvent. D) The solution will become saturated. E) none of the above